Linear polyubiquitylation of Gli protein regulates its protein stability and facilitates tumor growth in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 39164252
- PMCID: PMC11335874
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-024-02147-4
Linear polyubiquitylation of Gli protein regulates its protein stability and facilitates tumor growth in colorectal cancer
Abstract
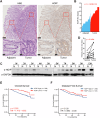
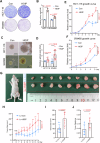
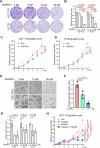
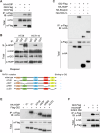
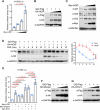
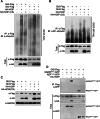
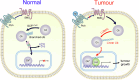
The linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC) mediates the linear ubiquitination of various proteins and is involved in NF-κB signaling and immune regulation. However, the function and mechanism of linear ubiquitination in regulating oncogenic signaling and tumor growth have remained poorly understood. Herein, we identified Gli proteins, key transcription factors in the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway, as novel substrates of LUBAC. Linear ubiquitination stabilizes Gli proteins, leading to the noncanonical activation of Hh signaling in CRC cells. Furthermore, LUBAC facilitates tumor growth in CRC cells. Additionally, elevated expression of LUBAC components in CRC tissues was observed, and higher expression levels of these components correlated with poor prognosis in CRC patients. Interestingly, inhibition of LUBAC using either a small molecule agonist or RNA silencing specifically suppressed cell growth in CRC cells but had no effect on normal intestinal cells. Taken together, aberrant expression of LUBAC components activates Hh signaling noncanonically by mediating linear ubiquitination, promoting tumor growth in CRC, demonstrating the novel function of linear ubiquitination in regulating the protein stability of its substrates and highlighting the potential of targeting LUBAC as a therapeutic strategy in CRC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Posttranslational Modification of HOIP Blocks Toll-Like Receptor 4-Mediated Linear-Ubiquitin-Chain Formation.mBio. 2015 Nov 17;6(6):e01777-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01777-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26578682 Free PMC article.
-
The Linear Ubiquitin Assembly Complex Modulates Latent Membrane Protein 1 Activation of NF-κB and Interferon Regulatory Factor 7.J Virol. 2017 Jan 31;91(4):e01138-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01138-16. Print 2017 Feb 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 27903798 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex and TAK1 kinase in A20 mutant Hodgkin lymphoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Nov 17;117(46):28980-28991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014470117. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33139544 Free PMC article.
-
Linear ubiquitination: a novel NF-κB regulatory mechanism for inflammatory and immune responses by the LUBAC ubiquitin ligase complex.Endocr J. 2012;59(8):641-52. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej12-0148. Epub 2012 May 19. Endocr J. 2012. PMID: 22673407 Review.
-
Role of Linear Ubiquitination in Health and Disease.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Jun;54(6):761-8. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0014TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26848516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- 31900559/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32260160/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82060517/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82160507/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32070783/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 31900550/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 20212ACB206009/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Jiangxi Province Natural Science Foundation)
- 20232ACB206034/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Jiangxi Province Natural Science Foundation)
- 20202BBG72003/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Jiangxi Province Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

