Influence of postruminal casein infusion and exogenous glucagon-like peptide 2 administration on the jejunal mucosal transcriptome in cattle
- PMID: 39146343
- PMCID: PMC11326568
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308983
Influence of postruminal casein infusion and exogenous glucagon-like peptide 2 administration on the jejunal mucosal transcriptome in cattle
Abstract
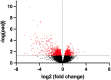
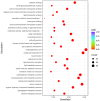
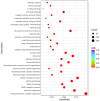
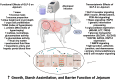
We previously demonstrated that postruminal casein infusion and exogenous glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) administration independently stimulated growth and carbohydrase activity of the pancreas and jejunal mucosa in cattle. The objective of the current study was to profile the jejunal mucosal transcriptome of cattle using next-generation RNA sequencing in response to postruminal casein infusion and exogenous GLP-2. Twenty-four Holstein steers [250 ± 23.1 kg body weight (BW)] received a continuous abomasal infusion of 3.94 g raw corn starch/kg of BW combined with either 0 or 1.30 g casein/kg of BW for 7 d. Steers received subcutaneous injections at 0800 and 2000 h to provide either 0 or 100 μg GLP-2/kg of BW per day. At the end of the 7-d treatment period, steers were slaughtered for collection of the jejunal mucosa. Total RNA was extracted from jejunal mucosal tissue, strand-specific cDNA libraries were prepared, and RNA sequencing was conducted to generate 150-bp paired-end reads at a depth of 40 M reads per sample. Differentially expressed genes (DEG), KEGG pathway enrichment, and gene ontology enrichment were determined based on the FDR-corrected P-value (padj). Exogenous GLP-2 administration upregulated (padj < 0.05) 667 genes and downregulated 1,101 genes of the jejunal mucosa. Sphingolipid metabolism, bile secretion, adherens junction, and galactose metabolism were among the top KEGG pathways enriched with upregulated DEG (padj < 0.05) in response to exogenous GLP-2 administration. The top gene ontologies enriched with upregulated DEG (padj < 0.05) in response to exogenous GLP-2 administration included nutrient metabolic processes, brush border and bicellular tight junction assembly, and enzyme and transporter activities. Exogenous GLP-2 administration increased or tended to increase (padj < 0.10) brush border carbohydrase (MGAM, LCT, TREH), hexose transporter (SLC5A1, SLC2A2), and associated transcription factor (HNF1, GATA4, KAT2B) mRNA expression of the jejunal mucosa. Gene ontologies and KEGG pathways that were downregulated (padj < 0.05) in response to exogenous GLP-2 were related to genetic information processing. Postruminal casein infusion downregulated (padj < 0.05) 7 jejunal mucosal genes that collectively did not result in enriched KEGG pathways or gene ontologies. This study highlights some of the transcriptional mechanisms associated with increased growth, starch assimilation capacity, and barrier function of the jejunal mucosa in response to exogenous GLP-2 administration.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postruminal Casein Infusion and Exogenous Glucagon-Like Peptide 2 Administration Differentially Stimulate Pancreatic α-Amylase and Small Intestinal α-Glucosidase Activity in Cattle.J Nutr. 2023 Oct;153(10):2854-2867. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2023.08.009. Epub 2023 Aug 10. J Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37573014
-
Duodenal Infusions of Starch with Casein or Glutamic Acid Influence Pancreatic and Small Intestinal Carbohydrase Activities in Cattle.J Nutr. 2020 Apr 1;150(4):784-791. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz319. J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31875476
-
Postruminal administration of partially hydrolyzed starch and casein influences pancreatic alpha-amylase expression in calves.J Nutr. 2002 Mar;132(3):376-81. doi: 10.1093/jn/132.3.376. J Nutr. 2002. PMID: 11880558
-
The small intestinal epithelia of beef steers differentially express sugar transporter messenger ribonucleic acid in response to abomasal versus ruminal infusion of starch hydrolysate.J Anim Sci. 2010 Jan;88(1):306-14. doi: 10.2527/jas.2009-1992. Epub 2009 Oct 9. J Anim Sci. 2010. PMID: 19820061 Clinical Trial.
-
Ruminal and abomasal starch hydrolysate infusions selectively decrease the expression of cationic amino acid transporter mRNA by small intestinal epithelia of forage-fed beef steers.J Dairy Sci. 2009 Mar;92(3):1124-35. doi: 10.3168/jds.2008-1521. J Dairy Sci. 2009. PMID: 19233805
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

