The Phoenix of stem cells: pluripotent cells in adult tissues and peripheral blood
- PMID: 39139297
- PMCID: PMC11319133
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1414156
The Phoenix of stem cells: pluripotent cells in adult tissues and peripheral blood
Abstract
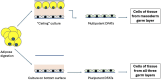
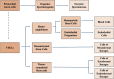
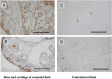
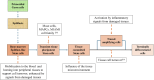
Pluripotent stem cells are defined as cells that can generate cells of lineages from all three germ layers, ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. On the contrary, unipotent and multipotent stem cells develop into one or more cell types respectively, but their differentiation is limited to the cells present in the tissue of origin or, at most, from the same germ layer. Multipotent and unipotent stem cells have been isolated from a variety of adult tissues, Instead, the presence in adult tissues of pluripotent stem cells is a very debated issue. In the early embryos, all cells are pluripotent. In mammalians, after birth, pluripotent cells are maintained in the bone-marrow and possibly in gonads. In fact, pluripotent cells were isolated from marrow aspirates and cord blood and from cultured bone-marrow stromal cells (MSCs). Only in few cases, pluripotent cells were isolated from other tissues. In addition to have the potential to differentiate toward lineages derived from all three germ layers, the isolated pluripotent cells shared other properties, including the expression of cell surface stage specific embryonic antigen (SSEA) and of transcription factors active in the early embryos, but they were variously described and named. However, it is likely that they are part of the same cell population and that observed diversities were the results of different isolation and expansion strategies. Adult pluripotent stem cells are quiescent and self-renew at very low rate. They are maintained in that state under the influence of the "niche" inside which they are located. Any tissue damage causes the release in the blood of inflammatory cytokines and molecules that activate the stem cells and their mobilization and homing in the injured tissue. The inflammatory response could also determine the dedifferentiation of mature cells and their reversion to a progenitor stage and at the same time stimulate the progenitors to proliferate and differentiate to replace the damaged cells. In this review we rate articles reporting isolation and characterization of tissue resident pluripotent cells. In the attempt to reconcile observations made by different authors, we propose a unifying picture that could represent a starting point for future experiments.
Keywords: SSEA3/4; VSELs; dedifferentiation; mesenchymal stem cells; muse cells; pluripotent genes; very small embryonic like cells.
Copyright © 2024 Cancedda and Mastrogiacomo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endogenous, very small embryonic-like stem cells: critical review, therapeutic potential and a look ahead.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Dec;23(1):41-76. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmw030. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 27614362 Review.
-
Mouse Bone Marrow VSELs Exhibit Differentiation into Three Embryonic Germ Lineages and Germ & Hematopoietic Cells in Culture.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017 Apr;13(2):202-216. doi: 10.1007/s12015-016-9714-0. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017. PMID: 28070859
-
Introduction to stem cells.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2023;199:3-32. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2023.02.012. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37678976 Review.
-
Adult reserve stem cells and their potential for tissue engineering.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2004;40(1):1-80. doi: 10.1385/CBB:40:1:1. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2004. PMID: 14983110 Review.
-
Multipotent/pluripotent stem cell populations in stromal tissues and peripheral blood: exploring diversity, potential, and therapeutic applications.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 May 12;15(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03752-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38735988 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahangar P., Mills S. J., Smith L. E., Strudwick X. L., Ting A. E., Vaes B., et al. (2020). Human multipotent adult progenitor cell-conditioned medium improves wound healing through modulating inflammation and angiogenesis in mice. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 11, 299. 10.1186/s13287-020-01819-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

