VolcanoSV enables accurate and robust structural variant calling in diploid genomes from single-molecule long read sequencing
- PMID: 39138168
- PMCID: PMC11322167
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51282-0
VolcanoSV enables accurate and robust structural variant calling in diploid genomes from single-molecule long read sequencing
Abstract
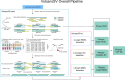
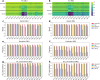
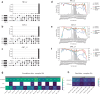
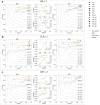
Structural variants (SVs) significantly contribute to human genome diversity and play a crucial role in precision medicine. Although advancements in single-molecule long-read sequencing offer a groundbreaking resource for SV detection, identifying SV breakpoints and sequences accurately and robustly remains challenging. We introduce VolcanoSV, an innovative hybrid SV detection pipeline that utilizes both a reference genome and local de novo assembly to generate a phased diploid assembly. VolcanoSV uses phased SNPs and unique k-mer similarity analysis, enabling precise haplotype-resolved SV discovery. VolcanoSV is adept at constructing comprehensive genetic maps encompassing SNPs, small indels, and all types of SVs, making it well-suited for human genomics studies. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that VolcanoSV surpasses state-of-the-art assembly-based tools in the detection of insertion and deletion SVs, exhibiting superior recall, precision, F1 scores, and genotype accuracy across a diverse range of datasets, including low-coverage (10x) datasets. VolcanoSV outperforms assembly-based tools in the identification of complex SVs, including translocations, duplications, and inversions, in both simulated and real cancer data. Moreover, VolcanoSV is robust to various evaluation parameters and accurately identifies breakpoints and SV sequences.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
VISTA: an integrated framework for structural variant discovery.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Jul 25;25(5):bbae462. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae462. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39297879 Free PMC article.
-
Tradeoffs in alignment and assembly-based methods for structural variant detection with long-read sequencing data.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 19;15(1):2447. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46614-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38503752 Free PMC article.
-
Longshot enables accurate variant calling in diploid genomes from single-molecule long read sequencing.Nat Commun. 2019 Oct 11;10(1):4660. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12493-y. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31604920 Free PMC article.
-
Haplotyping-Assisted Diploid Assembly and Variant Detection with Linked Reads.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2590:161-182. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2819-5_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36335499 Review.
-
Applications of advanced technologies for detecting genomic structural variation.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2023 Jul-Dec;792:108475. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2023.108475. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2023. PMID: 37931775 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

