Combination therapy of targeting CD20 antibody and immune checkpoint inhibitor may be a breakthrough in the treatment of B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 39130438
- PMCID: PMC11315150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34068
Combination therapy of targeting CD20 antibody and immune checkpoint inhibitor may be a breakthrough in the treatment of B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: CD20 is a membrane protein extensively expressed on the surface of B cells at various stages of development and differentiation. Herein, we conducted a bibliometrics analysis of the literature on CD20-targeting antibody therapy in lymphoma.
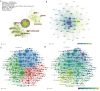
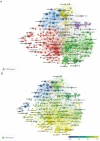
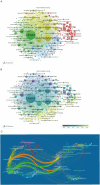
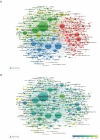
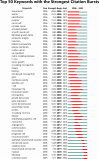
Methods: A total of 6663 articles were downloaded from the web of science core collection (WOSCC) from 1999 to July 23, 2022. Bibliometric.com was used for citation and annual publications analysis. VOSviewer was used to map countries/institutions/authors/journals nodes and links, extract hotspot keywords, and analyze the time trend of keywords. Citespace was employed to recognize the turning points based on the centrality value of countries, define the topic distribution of academics according to the map of dual-map overlay of journals, and characterize the emerging topics or landmark articles in a field based on references citation bursts.
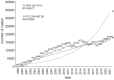
Results: All articles were cited 225,032 times, averaging 33.77. The number of articles increased from 1999 to 2002, while the growth rate entered the platform after 2002. The USA was the most publication country, and China was the largest emerging country. Hotspots in this field still focus on the efficacy of rituximab in treating non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and the pathogenesis of lymphoma Application of generation CD-20 antibodies or molecule inhibitors in clinical research and cellular therapy/immunotherapy, such as CAR-T and PDL1/PD1 were the emerging research topics.
Conclusion: This study provides essential information and the tendency of the CD20-targeting antibody therapy in lymphoma by using bibliometric and visual methods, which would provide helpful references for clinical experiments and basic scientific research.
Keywords: CD20; Combination therapy; Immunotherapy; Lymphoma; Rituximab.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
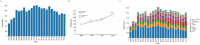


Similar articles
-
A bibliometric analysis of CD38-targeting antibody therapy in multiple myeloma from 1985 to 2021.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Apr;11(4):772-783. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1962. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35571665 Free PMC article.
-
Research hotspots and trends of bone defects based on Web of Science: a bibliometric analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Oct 8;15(1):463. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01973-3. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33032636 Free PMC article.
-
Worldwide productivity and research trend of publications concerning tumor immune microenvironment (TIME): a bibliometric study.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Jul 10;28(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01195-3. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37430294 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric study of immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1210802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1210802. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research trends of acupuncture therapy on facial paralysis in a decade spanning 2013-2023: A bibliometric analysis.Complement Ther Med. 2023 Dec;79:103006. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2023.103006. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Complement Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37972694 Review.
References
-
- Wu X., Zhang X., Feng W., Feng H., Ding Z., et al. A targeted Erythrocyte membrane-encapsulated drug-delivery system with anti-osteosarcoma and anti-osteolytic effects. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2021;13(24):27920–27933. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

