Exploring Intrinsic Disorder in Human Synucleins and Associated Proteins
- PMID: 39125972
- PMCID: PMC11313516
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158399
Exploring Intrinsic Disorder in Human Synucleins and Associated Proteins
Abstract
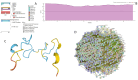
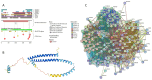
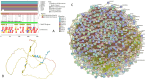
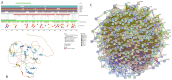
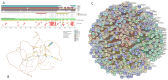
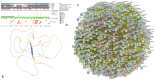
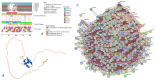
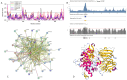
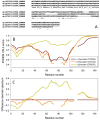
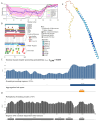
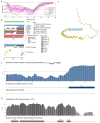
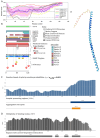
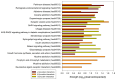
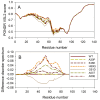
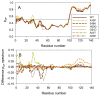
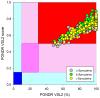
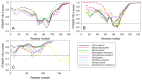
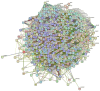
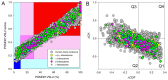
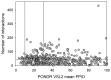
In this work, we explored the intrinsic disorder status of the three members of the synuclein family of proteins-α-, β-, and γ-synucleins-and showed that although all three human synucleins are highly disordered, the highest levels of disorder are observed in γ-synuclein. Our analysis of the peculiarities of the amino acid sequences and modeled 3D structures of the human synuclein family members revealed that the pathological mutations A30P, E46K, H50Q, A53T, and A53E associated with the early onset of Parkinson's disease caused some increase in the local disorder propensity of human α-synuclein. A comparative sequence-based analysis of the synuclein proteins from various evolutionary distant species and evaluation of their levels of intrinsic disorder using a set of commonly used bioinformatics tools revealed that, irrespective of their origin, all members of the synuclein family analyzed in this study were predicted to be highly disordered proteins, indicating that their intrinsically disordered nature represents an evolutionary conserved and therefore functionally important feature. A detailed functional disorder analysis of the proteins in the interactomes of the human synuclein family members utilizing a set of commonly used disorder analysis tools showed that the human α-synuclein interactome has relatively higher levels of intrinsic disorder as compared with the interactomes of human β- and γ- synucleins and revealed that, relative to the β- and γ-synuclein interactomes, α-synuclein interactors are involved in a much broader spectrum of highly diversified functional pathways. Although proteins interacting with three human synucleins were characterized by highly diversified functionalities, this analysis also revealed that the interactors of three human synucleins were involved in three common functional pathways, such as the synaptic vesicle cycle, serotonergic synapse, and retrograde endocannabinoid signaling. Taken together, these observations highlight the critical importance of the intrinsic disorder of human synucleins and their interactors in various neuronal processes.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; intrinsically disordered protein; liquid–liquid phase separation; protein–protein interactions; α-synuclein; β-synuclein; γ-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Localization of synucleins in the mammalian cochlea.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2008 Dec;9(4):452-63. doi: 10.1007/s10162-008-0134-y. Epub 2008 Jul 30. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2008. PMID: 18665422 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular ageing of alpha- and Beta-synucleins: protein damage and repair mechanisms.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 22;8(4):e61442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061442. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23630590 Free PMC article.
-
Monomeric synucleins generate membrane curvature.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 18;288(3):1829-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.418871. Epub 2012 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23184946 Free PMC article.
-
Fish Synucleins: An Update.Mar Drugs. 2015 Oct 30;13(11):6665-86. doi: 10.3390/md13116665. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26528989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The synucleins.Genome Biol. 2002;3(1):REVIEWS3002. doi: 10.1186/gb-2001-3-1-reviews3002. Epub 2001 Dec 20. Genome Biol. 2002. PMID: 11806835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

