Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase GhCDPK16 Exerts a Positive Regulatory Role in Enhancing Drought Tolerance in Cotton
- PMID: 39125876
- PMCID: PMC11311755
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158308
Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase GhCDPK16 Exerts a Positive Regulatory Role in Enhancing Drought Tolerance in Cotton
Abstract
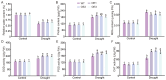
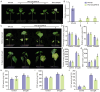
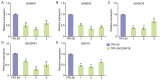
Cotton is essential for the textile industry as a primary source of natural fibers. However, environmental factors like drought present significant challenges to its cultivation, adversely affecting both production levels and fiber quality. Enhancing cotton's drought resilience has the potential to reduce yield losses and support the growth of cotton farming. In this study, the cotton calcium-dependent protein kinase GhCDPK16 was characterized, and the transcription level of GhCDPK16 was significantly upregulated under drought and various stress-related hormone treatments. Physiological analyses revealed that the overexpression of GhCDPK16 improved drought stress resistance in Arabidopsis by enhancing osmotic adjustment capacity and boosting antioxidant enzyme activities. In contrast, silencing GhCDPK16 in cotton resulted in increased dehydration compared with the control. Furthermore, reduced antioxidant enzyme activities and downregulation of ABA-related genes were observed in GhCDPK16-silenced plants. These findings not only enhanced our understanding of the biological functions of GhCDPK16 and the mechanisms underlying drought stress resistance but also underscored the considerable potential of GhCDPK16 in improving drought resilience in cotton.
Keywords: GhCDPK16; Gossypium hirsutum L.; drought stress; osmotic adjustment; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CDPK protein in cotton: genomic-wide identification, expression analysis, and conferring resistance to heat stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Sep 7;24(1):842. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05563-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39242989 Free PMC article.
-
Systematical characterization of Rab7 gene family in Gossypium and potential functions of GhRab7B3-A gene in drought tolerance.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 1;25(1):1023. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10930-x. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39482579 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of exogenous strigolactone application and strigolactone biosynthesis genes GhMAX3/GhMAX4b in response to drought tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Oct 26;24(1):1008. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05726-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39455926 Free PMC article.
-
Coping with drought: stress and adaptive mechanisms, and management through cultural and molecular alternatives in cotton as vital constituents for plant stress resilience and fitness.Biol Res. 2018 Nov 14;51(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s40659-018-0198-z. Biol Res. 2018. PMID: 30428929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Drought Stress Signaling in Plants and the Molecular Genetic Basis of Cotton Drought Tolerance.Cells. 2019 Dec 31;9(1):105. doi: 10.3390/cells9010105. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31906215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

