Genetic Mutations Associated With TNFAIP3 (A20) Haploinsufficiency and Their Impact on Inflammatory Diseases
- PMID: 39125844
- PMCID: PMC11311569
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158275
Genetic Mutations Associated With TNFAIP3 (A20) Haploinsufficiency and Their Impact on Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
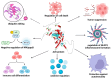
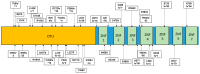
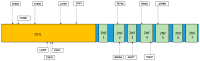
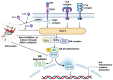
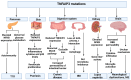
TNF-α-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3), commonly referred to as A20, is an integral part of the ubiquitin-editing complex that significantly influences immune regulation, apoptosis, and the initiation of diverse immune responses. The A20 protein is characterized by an N-terminal ovarian tumor (OTU) domain and a series of seven zinc finger (ZNF) domains. Mutations in the TNFAIP3 gene are implicated in various immune-related diseases, such as Behçet's disease, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune hepatitis, and rheumatoid arthritis. These mutations can lead to a spectrum of symptoms, including, but not limited to, recurrent fever, ulcers, rashes, musculoskeletal and gastrointestinal dysfunctions, cardiovascular issues, and respiratory infections. The majority of these mutations are either nonsense (STOP codon) or frameshift mutations, which are typically associated with immune dysfunctions. Nonetheless, missense mutations have also been identified as contributors to these conditions. These genetic alterations may interfere with several biological pathways, notably abnormal NF-κB signaling and dysregulated ubiquitination. Currently, there is no definitive treatment for A20 haploinsufficiency; however, therapeutic strategies can alleviate the symptoms in patients. This review delves into the mutations reported in the TNFAIP3 gene, the clinical progression in affected individuals, potential disease mechanisms, and a brief overview of the available pharmacological interventions for A20 haploinsufficiency. Mandatory genetic testing of the TNFAIP3 gene should be performed in patients diagnosed with autoinflammatory disorders to better understand the genetic underpinnings and guide treatment decisions.
Keywords: A20 haploinsufficiency; TNFAIP3 gene; autoimmunity; haploinsufficiency; immune dysfunctions; mutations; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Clinical Phenotypes in Haploinsufficiency A20 (HA20) With Disrupted Domains of A20.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 23;11:574992. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574992. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33101300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A20 Haploinsufficiency in a Chinese Patient With Intestinal Behcet's Disease-Like Symptoms: A Case Report.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 3;11:1414. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01414. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32719680 Free PMC article.
-
A novel missense mutation in TNFAIP3 causes haploinsufficiency of A20.Cell Immunol. 2022 Jan;371:104453. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2021.104453. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Cell Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34808442
-
Haploinsufficiency of A20 caused by a novel nonsense variant or entire deletion of TNFAIP3 is clinically distinct from Behçet's disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jun 4;21(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1928-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31164164 Free PMC article.
-
Haploinsufficiency of A20 (HA20): updates on the genetics, phenotype, pathogenesis and treatment.World J Pediatr. 2020 Dec;16(6):575-584. doi: 10.1007/s12519-019-00288-6. Epub 2019 Oct 5. World J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 31587140 Review.
References
-
- Schmitz R., Hansmann M.-L., Bohle V., Martin-Subero J.I., Hartmann S., Mechtersheimer G., Klapper W., Vater I., Giefing M., Gesk S., et al. TNFAIP3 (A20) is a tumor suppressor gene in Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2009;206:981–989. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090528. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

