Optimization of an Ischemic Retinopathy Mouse Model and the Consequences of Hypoxia in a Time-Dependent Manner
- PMID: 39125579
- PMCID: PMC11311598
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158008
Optimization of an Ischemic Retinopathy Mouse Model and the Consequences of Hypoxia in a Time-Dependent Manner
Abstract
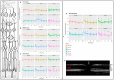
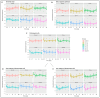
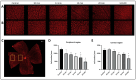
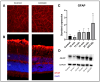
The retina is one of the highest metabolically active tissues with a high oxygen consumption, so insufficient blood supply leads to visual impairment. The incidence of related conditions is increasing; however, no effective treatment without side effects is available. Furthermore, the pathomechanism of these diseases is not fully understood. Our aim was to develop an optimal ischemic retinopathy mouse model to investigate the retinal damage in a time-dependent manner. Retinal ischemia was induced by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO) for 10, 13, 15 or 20 min, or by right permanent unilateral common carotid artery occlusion (UCCAO). Optical coherence tomography was used to follow the changes in retinal thickness 3, 7, 14, 21 and 28 days after surgery. The number of ganglion cells was evaluated in the central and peripheral regions on whole-mount retina preparations. Expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) was analyzed with immunohistochemistry and Western blot. Retinal degeneration and ganglion cell loss was observed in multiple groups. Our results suggest that the 20 min BCCAO is a good model to investigate the consequences of ischemia and reperfusion in the retina in a time-dependent manner, while the UCCAO causes more severe damage in a short time, so it can be used for testing new drugs.
Keywords: hypoxia; ischemia; retina.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Retinal Degeneration in a Murine Model of Retinal Ischemia by Unilateral Common Carotid Artery Occlusion.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Dec 31;2021:7727648. doi: 10.1155/2021/7727648. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 35005021 Free PMC article.
-
A mouse model of retinal hypoperfusion injury induced by unilateral common carotid artery occlusion.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Dec;201:108275. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108275. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32991884
-
Epac2-deficiency leads to more severe retinal swelling, glial reactivity and oxidative stress in transient middle cerebral artery occlusion induced ischemic retinopathy.Sci China Life Sci. 2015 Jun;58(6):521-30. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-4860-1. Epub 2015 May 19. Sci China Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25985753
-
Collapsin Response Mediator Protein-2-induced Retinal Ischemic Injury in a Novel Mice Model of Ocular Ischemia Syndrome.Chin Med J (Engl). 2017 Jun 5;130(11):1342-1351. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.206340. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017. PMID: 28524835 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular mechanisms of retinal ischemia].Vestn Oftalmol. 2010 May-Jun;126(3):59-64. Vestn Oftalmol. 2010. PMID: 20608206 Review. Russian.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

