Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluations of Novel Thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine Corticotropin Releasing Factor (CRF) Receptor Antagonists as Potential Treatments for Stress Related Disorders and Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
- PMID: 39125051
- PMCID: PMC11314199
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29153647
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluations of Novel Thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine Corticotropin Releasing Factor (CRF) Receptor Antagonists as Potential Treatments for Stress Related Disorders and Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
Abstract
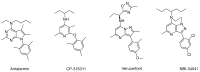
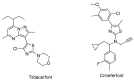
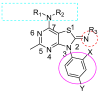
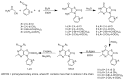
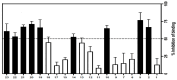
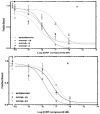
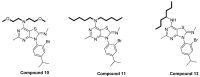
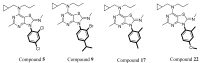
Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) is a key neuropeptide hormone that is secreted from the hypothalamus. It is the master hormone of the HPA axis, which orchestrates the physiological and behavioral responses to stress. Many disorders, including anxiety, depression, addiction relapse, and others, are related to over-activation of this system. Thus, new molecules that may interfere with CRF receptor binding may be of value to treat neuropsychiatric stress-related disorders. Also, CRF1R antagonists have recently emerged as potential treatment options for congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Previously, several series of CRF1 receptor antagonists were developed by our group. In continuation of our efforts in this direction, herein we report the synthesis and biological evaluation of a new series of CRF1R antagonists. Representative compounds were evaluated for their binding affinities compared to antalarmin. Four compounds (2, 5, 20, and 21) showed log IC50 values of -8.22, -7.95, -8.04, and -7.88, respectively, compared to -7.78 for antalarmin. This result indicates that these four compounds are superior to antalarmin by 2.5, 1.4, 1.7, and 1.25 times, respectively. It is worth mentioning that compound 2, in terms of IC50, is among the best CRF1R antagonists ever developed in the last 40 years. The in silico physicochemical properties of the lead compounds showed good drug-like properties. Thus, further research in this direction may lead to better and safer CRF receptor antagonists that may have clinical applications, particularly for stress-related disorders and the treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Keywords: CRF receptor antagonists; antalarmin; congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH); thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, structural optimization, SAR, in silico prediction of physicochemical properties and pharmacological evaluation of novel & potent thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptor antagonists.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022 Feb 1;169:106084. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2021.106084. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 34856350
-
Synthesis of substituted pyrimidines as corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptor ligands.Eur J Med Chem. 2014 May 6;78:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.03.040. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24675175
-
Don't stress about CRF: assessing the translational failures of CRF1antagonists.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 May;234(9-10):1467-1481. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4556-2. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28265716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of new thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidines as Corticotropin releasing factor modulators.Med Chem. 2014;11(1):50-9. doi: 10.2174/1573406410666140724115627. Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25059547 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances with the CRF1 receptor: design of small molecule inhibitors, receptor subtypes and clinical indications.Curr Pharm Des. 1999 May;5(5):289-315. Curr Pharm Des. 1999. PMID: 10213797 Review.
References
-
- Owens M.J., Nemeroff C.B. Physiology and pharmacology of corticotropin-releasing factor. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991;43:425–473. - PubMed
-
- Amano M. Handbook of Hormones: Comparative Endocrinology for Basic and Clinical Research. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2015. Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone; pp. 23–25. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

