Advanced Application of Polymer Nanocarriers in Delivery of Active Ingredients from Traditional Chinese Medicines
- PMID: 39124924
- PMCID: PMC11314021
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29153520
Advanced Application of Polymer Nanocarriers in Delivery of Active Ingredients from Traditional Chinese Medicines
Abstract
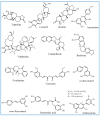
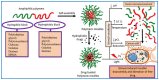
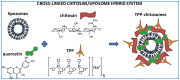
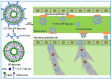
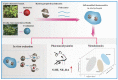
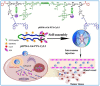
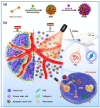
Active ingredients from Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs) have been a cornerstone of healthcare for millennia, offering a rich source of bioactive compounds with therapeutic potential. However, the clinical application of TCMs is often limited by challenges such as poor solubility, low bioavailability, and variable pharmacokinetics. To address these issues, the development of advanced polymer nanocarriers has emerged as a promising strategy for the delivery of TCMs. This review focuses on the introduction of common active ingredients from TCMs and the recent advancements in the design and application of polymer nanocarriers for enhancing the efficacy and safety of TCMs. We begin by discussing the unique properties of TCMs and the inherent challenges associated with their delivery. We then delve into the types of polymeric nanocarriers, including polymer micelles, polymer vesicles, polymer hydrogels, and polymer drug conjugates, highlighting their application in the delivery of active ingredients from TCMs. The main body of the review presents a comprehensive analysis of the state-of-the-art nanocarrier systems and introduces the impact of these nanocarriers on the solubility, stability, and bioavailability of TCM components. On the basis of this, we provide an outlook on the future directions of polymer nanocarriers in TCM delivery. This review underscores the transformative potential of polymer nanocarriers in revolutionizing TCM delivery, offering a pathway to harness the full therapeutic potential of TCMs while ensuring safety and efficacy in a modern medical context.
Keywords: Traditional Chinese Medicines; drug delivery; polymer drug conjugates; polymer hydrogels; polymer micelles; polymer vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advanced application of nanotechnology in active constituents of Traditional Chinese Medicines.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Nov 29;21(1):456. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02165-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 38017573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanocarriers for the delivery of active ingredients and fractions extracted from natural products used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2015 Jul;221:60-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2015.04.006. Epub 2015 May 5. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2015. PMID: 25999266 Review.
-
Nano-traditional Chinese medicine: a promising strategy and its recent advances.J Mater Chem B. 2022 Apr 20;10(16):2973-2994. doi: 10.1039/d2tb00225f. J Mater Chem B. 2022. PMID: 35380567 Review.
-
Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery System for Anticancer Active Ingredients from Traditional Chinese Medicines: A Review.Am J Chin Med. 2022;50(8):2011-2032. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X22500860. Am J Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 36414330 Review.
-
Advances in next-generation lipid-polymer hybrid nanocarriers with emphasis on polymer-modified functional liposomes and cell-based-biomimetic nanocarriers for active ingredients and fractions from Chinese medicine delivery.Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct;29:102237. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2020.102237. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32534047 Review.
References
-
- Zeng M., Guo D., Fernandez-Varo G., Zhang X., Fu S., Ju S., Yang H., Liu X., Wang Y.C., Zeng Y., et al. The Integration of Nanomedicine with Traditional Chinese Medicine: Drug Delivery of Natural Products and Other Opportunities. Mol. Pharm. 2023;20:886–904. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00882. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

