PD-L1 deglycosylation promotes its nuclear translocation and accelerates DNA double-strand-break repair in cancer
- PMID: 39122729
- PMCID: PMC11316045
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51242-8
PD-L1 deglycosylation promotes its nuclear translocation and accelerates DNA double-strand-break repair in cancer
Abstract
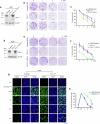
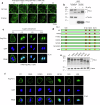
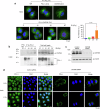
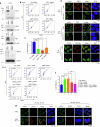
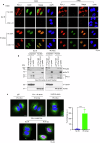
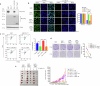
Resistance to radiotherapy is a major barrier during cancer treatment. Here using genome-scale CRISPR/Cas9 screening, we identify CD274 gene, which encodes PD-L1, to confer lung cancer cell resistance to ionizing radiation (IR). Depletion of endogenous PD-L1 delays the repair of IR-induced DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and PD-L1 loss downregulates non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) while overexpression of PD-L1 upregulates NHEJ. IR induces translocation of PD-L1 from the membrane into nucleus dependent on deglycosylation of PD-L1 at N219 and CMTM6 and leads to PD-L1 recruitment to DSBs foci. PD-L1 interacts with Ku in the nucleus and enhances Ku binding to DSB DNA. The interaction between the IgC domain of PD-L1 and the core domain of Ku is required for PD-L1 to accelerate NHEJ-mediated DSB repair and produce radioresistance. Thus, PD-L1, in addition to its immune inhibitory activity, acts as mechanistic driver for NHEJ-mediated DSB repair in cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Roles for the DNA-PK complex and 53BP1 in protecting ends from resection during DNA double-strand break repair.J Radiat Res. 2020 Sep 8;61(5):718-726. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rraa053. J Radiat Res. 2020. PMID: 32779701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOXL2 directs DNA double-strand break repair pathways by differentially interacting with Ku.Nat Commun. 2020 Apr 24;11(1):2010. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15748-1. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32332759 Free PMC article.
-
Ku70 suppresses alternative end joining in G1-arrested progenitor B cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 May 25;118(21):e2103630118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2103630118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34006647 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Induced Double-Strand Break Repair in Arabidopsis Nonhomologous End-Joining Mutants.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Jan 5;7(1):193-202. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.035204. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 27866150 Free PMC article.
-
Microhomology-mediated end joining: Good, bad and ugly.Mutat Res. 2018 May;809:81-87. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 16. Mutat Res. 2018. PMID: 28754468 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

