Trends, costs, and complications associated with after-hours surgery and unscheduled hospitalization in spinal surgery
- PMID: 39117344
- PMCID: PMC11309809
- DOI: 10.1302/2633-1462.58.BJO-2024-0026.R1
Trends, costs, and complications associated with after-hours surgery and unscheduled hospitalization in spinal surgery
Abstract
Aims: The escalating demand for medical resources to address spinal diseases as society ages is an issue that requires careful evaluation. However, few studies have examined trends in spinal surgery, especially unscheduled hospitalizations or surgeries performed after hours, through large databases. Our study aimed to determine national trends in the number of spine surgeries in Japan. We also aimed to identify trends in after-hours surgeries and unscheduled hospitalizations and their impact on complications and costs.
Methods: We retrospectively investigated data extracted from the Diagnosis Procedure Combination database, a representative inpatient database in Japan. The data from April 2010 to March 2020 were used for this study. We included all patients who had undergone any combination of laminectomy, laminoplasty, discectomy, and/or spinal arthrodesis.
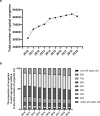
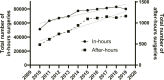
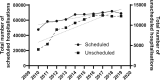
Results: This investigation included 739,474 spinal surgeries and 739,215 hospitalizations in Japan. There was an average annual increase of 4.6% in the number of spinal surgeries. Scheduled hospitalizations increased by 3.7% per year while unscheduled hospitalizations increased by 11.8% per year. In-hours surgeries increased by 4.5% per year while after-hours surgeries increased by 9.9% per year. Complication rates and costs increased for both after-hours surgery and unscheduled hospitalizations, in comparison to their respective counterparts of in-hours surgery and scheduled hospitalizations.
Conclusion: This study provides important insights for those interested in improving spine care in an ageing society. The swift surge in after-hours spinal surgeries and unscheduled hospitalizations highlights that the medical needs of an increasing number of patients due to an ageing society are outpacing the capacity of existing medical resources.
© 2024 Tanaka et al.
Conflict of interest statement
H. Inose reports that until March 2023, his department was receiving funding for operating costs from Medtronic and Stryker, which is unrelated to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Out-of-hours emergent surgery for degenerative spinal disease in Canada: a retrospective cohort study from a national registry.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024 Jun 11;36:100816. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2024.100816. eCollection 2024 Aug. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024. PMID: 38966387 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality and morbidity in dialysis-dependent patients undergoing spinal surgery: analysis of a national administrative database in Japan.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 Mar 7;94(5):433-8. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.00183. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012. PMID: 22398737
-
Surgical treatment of early-onset idiopathic scoliosis in the United States: a trend analysis of 15 years (1997-2012).Spine J. 2019 Feb;19(2):314-320. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.05.033. Epub 2018 May 23. Spine J. 2019. PMID: 29802889
-
National Trends in Spinal Fusion Surgery For Scheuermann Kyphosis.Spine Deform. 2015 Jan;3(1):52-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jspd.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Spine Deform. 2015. PMID: 27927452
-
The Impact of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Canada 2018: Direct Costs and Health Services Utilization.J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb;2(Suppl 1):S17-S33. doi: 10.1093/jcag/gwy055. Epub 2018 Nov 2. J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31294382 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

