Retrospective identification of the first cord blood-transplanted severe aplastic anemia in a STAT1-associated chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis family: case report, review of literature and pathophysiologic background
- PMID: 39114664
- PMCID: PMC11303233
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1430938
Retrospective identification of the first cord blood-transplanted severe aplastic anemia in a STAT1-associated chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis family: case report, review of literature and pathophysiologic background
Abstract
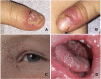
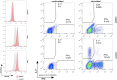
Severe aplastic anemia (SAA) is a life-threatening bone marrow failure syndrome whose development can be triggered by environmental, autoimmune, and/or genetic factors. The latter comprises germ line pathogenic variants in genes that bring about habitually predisposing syndromes as well as immune deficiencies that do so only occasionally. One of these disorders is the autosomal dominant form of chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMC), which is defined by germ line STAT1 gain-of-function (GOF) pathogenic variants. The resultant overexpression and constitutive activation of STAT1 dysregulate the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT) signaling pathway, which normally organizes the development and proper interaction of different components of the immunologic and hematopoietic system. Although SAA is an extremely rare complication in this disorder, it gained a more widespread interest when it became clear that the underlying causative pathomechanism may, in a similar fashion, also be instrumental in at least some of the idiopathic SAA cases. Based on these premises, we present herein what is the historically most likely first cord blood-transplanted SAA case in a CMC family with a documented STAT1 GOF pathogenic variant. In addition, we recapitulate the characteristics of the six CMC SAA cases that have been reported so far and discuss the significance of STAT1 GOF pathogenic variants and other STAT1 signaling derangements in the context of these specific types of bone marrow failure syndromes. Because a constitutively activated STAT1 signaling, be it driven by STAT1 GOF germ line pathogenic variants or any other pathogenic variant-independent events, is apparently important for initiating and maintaining the SAA disease process, we propose to acknowledge that SAA is one of the definite disease manifestations in STAT1-mutated CMC cases. For the same reason, we deem it necessary to also incorporate molecular and functional analyses of STAT1 into the diagnostic work-up of SAA cases.
Keywords: STAT1; chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMC); gain-of-function pathogenic variant; severe aplastic anemia (SAA); transplantation.
Copyright © 2024 Fink, Höpfl, Witsch-Baumgartner, Kropshofer, Martin, Fink, Heeg, Peters, Zschocke and Haas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Extended Clinical Phenotype of 26 Patients with Chronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis due to Gain-of-Function Mutations in STAT1.J Clin Immunol. 2016 Jan;36(1):73-84. doi: 10.1007/s10875-015-0214-9. Epub 2015 Nov 25. J Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26604104 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese Pedigree of Chronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis Due to STAT1 Gain-of-Function Mutation: A Case Study and Literature Review.Mycopathologia. 2023 Apr;188(1-2):87-97. doi: 10.1007/s11046-022-00685-y. Epub 2022 Nov 6. Mycopathologia. 2023. PMID: 36335528 Review.
-
Utility of Ruxolitinib in a Child with Chronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis Caused by a Novel STAT1 Gain-of-Function Mutation.J Clin Immunol. 2018 Jul;38(5):589-601. doi: 10.1007/s10875-018-0519-6. Epub 2018 Jun 22. J Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29934865
-
Bronchiectasis and Recurrent Respiratory Infections with a De Novo STAT1 Gain-of-Function Variant: First Case in Korea.Yonsei Med J. 2018 Oct;59(8):1004-1007. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.1004. Yonsei Med J. 2018. PMID: 30187709 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment options for chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis.J Infect. 2016 Jul 5;72 Suppl:S56-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2016.04.023. Epub 2016 May 6. J Infect. 2016. PMID: 27161991 Review.
References
-
- Fiesco-Roa MO, Garcia-de Teresa B, Leal-Anaya P, van 't Hek R, Wegman-Ostrosky T, Frias S, et al. . Fanconi anemia and dyskeratosis congenita/telomere biology disorders: Two inherited bone marrow failure syndromes with genomic instability. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:12949435. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.949435 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

