The PerioGene North Study Uncovers Serum Proteins Related to Periodontitis
- PMID: 39101637
- PMCID: PMC11402264
- DOI: 10.1177/00220345241263320
The PerioGene North Study Uncovers Serum Proteins Related to Periodontitis
Abstract
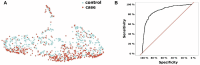
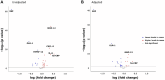
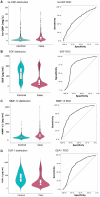
The sequalae of periodontitis include irreversible degradation of tooth-supporting structures and circulatory spread of inflammatory mediators. However, the serum protein profile in periodontitis is not well described, which is partly attributable to the limited number of studies based on large and well-characterized periodontitis cohorts. This study aims to identify novel, circulating inflammation-related proteins associated with periodontitis within the PerioGene North case-control study, which includes 478 cases with severe periodontitis and 509 periodontally healthy controls. The serum concentrations of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and a panel of 45 inflammation-related proteins were analyzed using targeted proteomics. A distinguishable serum protein profile was evident in periodontitis cases. The protein pattern could separate cases from controls with a sensitivity of 0.81 and specificity of 0.81 (area under the curve = 0.87). Adjusted levels for hs-CRP and 24 of the 45 proteins were different between cases and controls. High levels of hs-CRP and matrix metalloproteinase-12, and low levels of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1 (OLR-1) were detected among the cases. Furthermore, the levels of C-C motif chemokine-19, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-3 (CSF-3), interleukin-7 (IL-7), and hs-CRP were significantly higher in cases with a high degree of gingival inflammation. The levels of CSF-3 and tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member-10 TNFSF-10 were higher in cases with many deep periodontal pockets. The PerioGene North study includes detailed clinical periodontal data and uncovers a distinct serum protein profile in periodontitis. The findings of lower EGF and OLR-1 among the cases are highlighted, as this has not been presented before. The role of EGF and OLR-1 in periodontitis pathogenesis and as possible future biomarkers should be further explored.
Keywords: biomarkers; bone loss; epidemiology; inflammation; periodontal disease; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is the severity of periodontitis related to gingival crevicular fluid and serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein concentrations?Clin Lab. 2014;60(10):1653-8. doi: 10.7754/clin.lab.2014.131217. Clin Lab. 2014. PMID: 25651710
-
Periodontitis-associated up-regulation of systemic inflammatory mediator level may increase the risk of coronary heart disease.J Periodontal Res. 2010 Feb;45(1):116-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2009.01209.x. Epub 2009 Jul 8. J Periodontal Res. 2010. PMID: 19602107
-
Effect of periodontal treatment on the C-reactive protein and proinflammatory cytokine levels in Japanese periodontitis patients.J Periodontal Res. 2005 Feb;40(1):53-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2004.00772.x. J Periodontal Res. 2005. PMID: 15613080
-
Increased serum PCSK9, a potential biomarker to screen for periodontitis, and decreased total bilirubin associated with probing depth in a Japanese community survey.J Periodontal Res. 2018 Jun;53(3):446-456. doi: 10.1111/jre.12533. Epub 2018 Mar 8. J Periodontal Res. 2018. PMID: 29516504
-
Does Obstructive Sleep Apnea Increase the Risk for Periodontal Disease? A Case-Control Study.J Periodontol. 2017 May;88(5):443-449. doi: 10.1902/jop.2016.160365. Epub 2016 Nov 18. J Periodontol. 2017. PMID: 27858556
References
-
- Armitage GC. 1999. Development of a classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions. Ann Periodontol. 4(1):1–6. - PubMed
-
- Bellac CL, Dufour A, Krisinger MJ, Loonchanta A, Starr AE, Auf dem Keller U, Lange PF, Goebeler V, Kappelhoff R, Butler GS, et al.. 2014. Macrophage matrix metalloproteinase-12 dampens inflammation and neutrophil influx in arthritis. Cell Rep. 9(2):618–632. - PubMed
-
- Bjornfot Holmstrom S, Clark R, Zwicker S, Bureik D, Kvedaraite E, Bernasconi E, Nguyen Hoang AT, Johannsen G, Marsland BJ, Bostrom EA, et al.. 2017. Gingival tissue inflammation promotes increased matrix metalloproteinase-12 production by CD200R(low) monocyte-derived cells in periodontitis. J Immunol. 199(12):4023–4035. - PubMed
-
- Bostrom EA, Kindstedt E, Sulniute R, Palmqvist P, Majster M, Holm CK, Zwicker S, Clark R, Onell S, Johansson I, et al.. 2015. Increased Eotaxin and MCP-1 levels in serum from individuals with periodontitis and in human gingival fibroblasts exposed to pro-inflammatory cytokines. PloS One. 10(8):e0134608. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

