Association between serum albumin and body water using a bioelectrical impedance analyzer: a case report of longitudinal variation in a child with initial idiopathic nephrotic syndrome
- PMID: 39091551
- PMCID: PMC11292089
- DOI: 10.21037/acr-23-211
Association between serum albumin and body water using a bioelectrical impedance analyzer: a case report of longitudinal variation in a child with initial idiopathic nephrotic syndrome
Abstract
Background: Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) is a commonly used noninvasive technique for body composition assessment with recently expanded indications. This reproducible measurement method uses electrical conductivity to evaluate body composition, including fluid status. In pediatric idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS), albumin leaks into the urine, resulting in dysregulated colloid-osmotic pressure in the blood vessels. This results in decreased circulating blood volume and edema. Blood tests are a useful evaluation method; however, it cannot be performed frequently in children because of their invasive nature. Herein, we present a case of a child with INS demonstrating a longitudinal correlation between serum albumin (S-Alb) levels and extracellular water (ECW)/total body water (TBW) ratio.
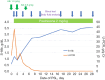
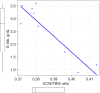
Case description: A 6-year-old boy was admitted to the hospital for INS treatment after informed consent was obtained. He presented with severe proteinuria symptoms and an increased weight of 3 kg before the onset of INS. Standard treatment with prednisolone (PSL) for 28 days was initiated, and his proteinuria resolved on day 7. During the acute course, albumin replacement was conducted thrice for fluid management purposes and did not cause severe intravascular dehydration. The fluid composition was assessed over time; each measurement lasted for approximately 10 minutes and was performed on the same day as the blood tests. Nine measurements were taken, and S-Alb levels and the ECW/TBW ratio (r=-0.72, P<0.04) exhibited a significant negative correlation.
Conclusions: BIA can potentially predict S-Alb levels objectively and noninvasively within a short period. Although further validation is needed, this measurement can reduce the invasiveness of testing in children with INS.
Keywords: Body composition; case report; nephrotic syndrome (NS); pediatrics; serum albumin (S-Alb).
2024 AME Case Reports. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://acr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/acr-23-211/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of body composition using dry mass index and ratio of total body water to estimated volume based on bioelectrical impedance analysis in chronic kidney disease patients.J Ren Nutr. 2013 Jan;23(1):28-36. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2011.12.006. Epub 2012 Mar 9. J Ren Nutr. 2013. PMID: 22406124
-
The role of bioelectrical impedance analysis, NT-ProBNP and inferior vena cava sonography in the assessment of body fluid volume in children with nephrotic syndrome.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2018 Jan-Feb;38(1):48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.nefro.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2018. PMID: 28751054 English, Spanish.
-
Early detection of subclinical edema in chronic kidney disease patients by bioelectrical impedance analysis.J Med Assoc Thai. 2014 Nov;97 Suppl 11:S1-10. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014. PMID: 25509689
-
Body fluid volumes measurements by impedance: A review of bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) and bioimpedance analysis (BIA) methods.Med Eng Phys. 2008 Dec;30(10):1257-69. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2008.06.009. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Med Eng Phys. 2008. PMID: 18676172 Review.
-
Bioimpedance spectrometry in the determination of body water compartments: accuracy and clinical significance.Appl Radiat Isot. 1998 May-Jun;49(5-6):447-55. doi: 10.1016/s0969-8043(97)00052-3. Appl Radiat Isot. 1998. PMID: 9569513 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Nutritional Status and Metabolic Imbalances in Children with FASD: A Cross-Sectional Study.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 7;16(19):3401. doi: 10.3390/nu16193401. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39408368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hori T, Nakamura S, Yamagami H, et al. Phase angle and extracellular water-to-total body water ratio estimated by bioelectrical impedance analysis are associated with levels of hemoglobin and hematocrit in patients with diabetes. Heliyon 2023;9:e14724. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14724 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
