Correlation of MicroRNA-125b, Sirtuin, and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 with Biochemical Parameters and Risk Factors in Atherosclerosis Patients
- PMID: 39086582
- PMCID: PMC11288231
- DOI: 10.61186/rbmb.12.4.631
Correlation of MicroRNA-125b, Sirtuin, and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 with Biochemical Parameters and Risk Factors in Atherosclerosis Patients
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerosis (AS) is an inflammatory disease linked to vascular events, with dysregulation of microRNA (miR)-125b, contributing to cardiovascular disease pathogenesis. Moreover, there is evidence of the involvement of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) in AS. This study aimed to survey the expression levels of miR-125b, STAT3, and SIRT6 in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of AS patients and controls, and to find their correlations with biochemical parameters and risk factors.
Methods: This study included blood samples from 45 controls and 45 AS patients, with PBMCs isolated using Ficoll solution. Expression levels of miR-125b, STAT3, and SIRT6 were determined via quantitative Real Time-PCR.
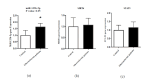
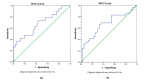
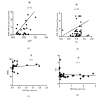
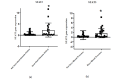
Results: The findings revealed a significant increase in miR-125b levels in patients compared to controls (P = 0.017). However, alterations in STAT3 and SIRT6 expression were not significant (P> 0.05). There was no substantial relationship between miR-125b and STAT3 (P = 0.522) or SIRT6 (P = 0.88). miR-125b showed a significant relationship with atherogenic indexes and creatinine (P<0.05), while the association of SIRT6 with HDL and creatinine was significant (P<0.05). STAT3 exhibited high diagnostic power for identifying individuals at risk of heart disease and hypertension (P<0.05).
Conclusion: STAT3 can serve as a valuable biomarker for detecting AS and AS-related risk factors. miR-125b and SIRT6 may be associated with AS lipid metabolism. However, further studies with larger sample sizes are recommended to mechanistically elucidate the association of these genes.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Leukocyte; SIRT6; STAT3; microRNA-125b.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-125b exerts antitumor functions in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by targeting the STAT3 pathway.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020 Mar 5;25:12. doi: 10.1186/s11658-020-00207-y. eCollection 2020. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32161621 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of methylation of MicroRNA-122, -125b and -106b in regulation of Cyclin G1, CAT-1 and STAT3 target genes in isoniazid-induced liver injury.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Mar 20;19(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40360-018-0201-x. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29554950 Free PMC article.
-
CircVAPA contributes to hyper-proliferation and inflammation of keratinocytes through miR-125b-5p/sirt6 axis in psoriasis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Feb;115:109632. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109632. Epub 2022 Dec 31. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36592530
-
MiR-125b attenuates human hepatocellular carcinoma malignancy through targeting SIRT6.Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Jun 1;8(6):993-1007. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30034937 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-125b-5p Suppresses Hypothyroidism Development by Targeting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Jul 20;24:5041-5049. doi: 10.12659/MSM.907510. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30027933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kattoor AJ, Pothineni NVK, Palagiri D, Mehta JL. Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. . Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2017;19(11):42. - PubMed
-
- Khyzha N, Alizada A, Wilson MD, Fish JE. Epigenetics of atherosclerosis: emerging mechanisms and methods. . Trends Mol Med. . 2017;23(4):332–347. - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh S, Mirshafiey A, Djalali M, Alvandi E, Mohammadzadeh Honarvar N, Javanbakht MH. Vitamin D3 induces gene expression of Ox-LDL scavenger receptors in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat aortas: new insight into the role of vitamin D in diabetic atherosclerosis. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. . 2018;6(2):170–177. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
