Current perspectives on mesenchymal stem cells as a potential therapeutic strategy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 39086561
- PMCID: PMC11287429
- DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i7.760
Current perspectives on mesenchymal stem cells as a potential therapeutic strategy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
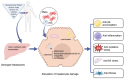
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has emerged as a significant health challenge, characterized by its widespread prevalence, intricate natural progression and multifaceted pathogenesis. Although NAFLD initially presents as benign fat accumulation, it may progress to steatosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are recognized for their intrinsic self-renewal, superior biocompatibility, and minimal immunogenicity, positioning them as a therapeutic innovation for liver diseases. Therefore, this review aims to elucidate the potential roles of MSCs in alleviating the progression of NAFLD by alteration of underlying molecular pathways, including glycolipid metabolism, inflammation, oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and fibrosis. The insights are expected to provide further understanding of the potential of MSCs in NAFLD therapeutics, and support the development of MSC-based therapy in the treatment of NAFLD.
Keywords: Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Fibrosis; Inflammation; Lipid accumulation; Mesenchymal stem cells; Non-alcoholic induced fatty liver disease; Oxidative stress.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Innovative mesenchymal stem cell treatments for fatty liver disease.World J Stem Cells. 2024 Sep 26;16(9):846-853. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i9.846. World J Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 39351260 Free PMC article.
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate liver steatosis by promoting fatty acid oxidation and reducing fatty acid synthesis.JHEP Rep. 2023 Mar 28;5(7):100746. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100746. eCollection 2023 Jul. JHEP Rep. 2023. PMID: 37274776 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic signatures across the full spectrum of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.JHEP Rep. 2022 Mar 26;4(5):100477. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100477. eCollection 2022 May. JHEP Rep. 2022. PMID: 35434590 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in innate immune cells - a significant contribution to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 22;13:951406. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.951406. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35958574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: current perspectives and recent advances.J Pathol. 2017 Jan;241(1):36-44. doi: 10.1002/path.4829. Epub 2016 Nov 22. J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27757953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Attenuate Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance in Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Activating the FGF21-Adiponectin Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 27;25(19):10447. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910447. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408777 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells in liver regeneration: Insights and future directions.World J Stem Cells. 2024 Sep 26;16(9):842-845. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i9.842. World J Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 39351263 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative mesenchymal stem cell treatments for fatty liver disease.World J Stem Cells. 2024 Sep 26;16(9):846-853. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i9.846. World J Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 39351260 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells: A promising therapeutic avenue for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.World J Stem Cells. 2024 Aug 26;16(8):780-783. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i8.780. World J Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 39219724 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the functionality of mesenchymal stem cells: An attractive treatment strategy for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease?World J Stem Cells. 2024 Oct 26;16(10):854-859. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i10.854. World J Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 39493827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Younossi ZM, Golabi P, de Avila L, Paik JM, Srishord M, Fukui N, Qiu Y, Burns L, Afendy A, Nader F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2019;71:793–801. - PubMed
-
- Domingues I, Leclercq IA, Beloqui A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Current therapies and future perspectives in drug delivery. J Control Release. 2023;363:415–434. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

