Three-dimensional cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuate pulmonary fibrosis by improving the balance of mitochondrial fusion and fission
- PMID: 39077914
- PMCID: PMC11386227
- DOI: 10.1093/stcltm/szae051
Three-dimensional cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuate pulmonary fibrosis by improving the balance of mitochondrial fusion and fission
Abstract
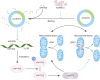
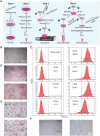
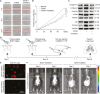
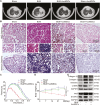
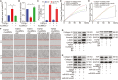
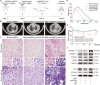
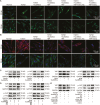
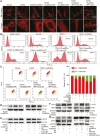
Pulmonary fibrosis is a kind of fibrotic interstitial pneumonia with poor prognosis. Aging, environmental pollution, and coronavirus disease 2019 are considered as independent risk factors for pulmonary fibrogenesis. Consequently, the morbidity and mortality striking continues to rise in recent years. However, the clinical therapeutic efficacy is very limited and unsatisfactory. So it is necessary to develop a new effective therapeutic approach for pulmonary fibrosis. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hucMSCs) are considered as a promising treatment for various diseases because of their multiple differentiation and immunomodulatory function. The key bottleneck in the clinical application of hucMSCs therapy is the high-quality and large-scale production. This study used FloTrix miniSpin bioreactor, a three-dimensional (3D) cell culture system, for large-scale expansion of hucMSCs in vitro, and proved 3D cultured hucMSCs inhibited the differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and myofibroblasts proliferation and migration, leading to slow down the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Further mechanistic studies clarified that hucMSCs reduced the amount of binding between circELP2 and miR-630, resulting in blocking YAP/TAZ translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus. This condition inhibited mitochondrial fusion and promoted mitochondrial fission, and ultimately improved fusion/fission balance and cellular homeostasis. To sum up, this work clarified the anti-fibrosis and mechanism of hucMSCs cultured from the 3D FloTrix miniSpin bioreactor. We hope to provide new ideas and new methods for the clinical transformation and industrialization of hucMSCs therapy.
Keywords: YAP/TAZ; circRNA; hucMSCs; mitochondrial fission; mitochondrial fusion; pulmonary fibrosis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
hucMSCs Treatment Ameliorated Pulmonary Fibrosis via Downregulating the circFOXP1-HuR-EZH2/STAT1/FOXK1 Autophagic Axis.Stem Cells. 2023 Oct 8;41(10):928-943. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxad053. Stem Cells. 2023. PMID: 37419489
-
The human umbilical cord stem cells improve the viability of OA degenerated chondrocytes.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Mar;17(3):4474-4482. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8413. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29328479 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of endothelial function and attenuation of portal vein injury using mesenchymal stem cells carrying miRNA-25-3p.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 2;14(1):15113. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64263-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38956421 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Osteogenesis-Related Regulatory Mechanisms of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Jul;19(5):1252-1267. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10521-5. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 36917312 Review.
-
Sources, Identification, and Clinical Implications of Heterogeneity in Human Umbilical Cord Stem Cells.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1169:243-256. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-24108-7_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31487028 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

