Response of FGFR-2 Positive Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma to Futibatinib: A Case Report
- PMID: 39077220
- PMCID: PMC11283924
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.63332
Response of FGFR-2 Positive Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma to Futibatinib: A Case Report
Abstract
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) is an uncommon and aggressive head and neck cancer mainly affecting minor salivary glands. It affects more women than men in their 60s and 70s. The tumor is typically locally aggressive and has a high rate of distant metastatic disease. This report unveils a potential avenue for targeted therapy for the management of metastatic disease: a patient with ACC who harbored a specific fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR-2) mutation and responded significantly to a novel FGFR-2 inhibitor. This finding could pave the way for personalized treatment options for ACC patients with similar genetic alterations. Nevertheless, the use of futibatinib requires further investigation to optimize treatment protocols, including exploring combination therapies, identifying predictive biomarkers for treatment response, and developing strategies to overcome potential resistance.
Keywords: adenoid cystic carcinoma (acc); fibroblast growth factor inhibitor; fibroblast growth factor receptor (fgfr); futibatinib; salivary gland tumor.
Copyright © 2024, Rodriguez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
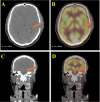
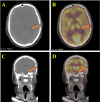
Similar articles
-
Futibatinib, an Irreversible FGFR1-4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of FGFR-Aberrant Tumors.Oncologist. 2023 Nov 2;28(11):928-943. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad149. Oncologist. 2023. PMID: 37390492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Futibatinib Is a Novel Irreversible FGFR 1-4 Inhibitor That Shows Selective Antitumor Activity against FGFR-Deregulated Tumors.Cancer Res. 2020 Nov 15;80(22):4986-4997. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2568. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32973082
-
Current opinions on diagnosis and treatment of adenoid cystic carcinoma.Oral Oncol. 2022 Jul;130:105945. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2022.105945. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Oral Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35662026 Review.
-
As2O3 may be a treatment option for adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary gland.Med Hypotheses. 2010 Dec;75(6):490-1. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2010.07.001. Epub 2010 Jul 24. Med Hypotheses. 2010. PMID: 20656411
-
Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the mobile tongue: A rare case.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2012 Dec;9(Suppl 1):S115-8. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2012. PMID: 23814551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FGFR-targeted therapeutics: clinical activity, mechanisms of resistance and new directions. Katoh M, Loriot Y, Brandi G, Tavolari S, Wainberg ZA, Katoh M. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2024;21:312–319. - PubMed
-
- Fibroblast growth factor receptors as treatment targets in clinical oncology. Katoh M. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16:105–122. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
