Systolic Pulmonary Artery Pressure and Cardiovascular Biomarkers-New Non-Invasive Ways to Detect Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis Undergoing TAVR?
- PMID: 39076911
- PMCID: PMC11266760
- DOI: 10.31083/j.rcm2307224
Systolic Pulmonary Artery Pressure and Cardiovascular Biomarkers-New Non-Invasive Ways to Detect Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis Undergoing TAVR?
Abstract
Background: Patients with severe aortic valve stenosis (AS) frequently present with pulmonary hypertension (PH). The gold standard for detection of pulmonary hypertension is right heart catheterization, which is not routinely performed as a preoperative standard in cardiology centers today, neither before surgical valve replacement nor before transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) procedure. Echocardiographic determination of systolic pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP) provides an opportunity to assess the presence or absence of PH. The aim of the present study was to investigate the extent to which plasma levels of common cardiovascular biomarkers behave in patients with severe AS and an sPAP 40 mmHg in comparison to patients with an sPAP 40 mmHg.
Methods: 179 patients with echocardiographic evidence of severe AS before TAVR procedure were divided into 2 groups based on sPAP. An sPAP of 40 mmHg was considered the cut-off value, with absence of PH defined by an sPAP 40 mmHg (n = 82) and presence of PH defined by an sPAP 40 mmHg (n = 97). Directly before TAVR, a blood sample was drawn from each patient, and plasma concentrations of the cardiovascular biomarkers Soluble Suppression of Tumorigenicity-2 (sST2), Growth/Differentiation of Factor-15 (GDF-15), Heart-Type Fatty-Acid Binding Protein (H-FABP), Insulin Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 (IGF-BP2), Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor (suPAR), Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) and Cardiac Troponin I (cTnI) were determined.
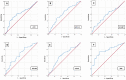
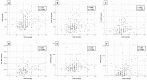
Results: Patients with an sPAP 40 mmHg had significantly higher sST2 (p = 0.010), GDF-15 (p = 0.005), IGF-BP2 (p = 0.029), suPAR (p = 0.018), BNP (p 0.001) and cTnI (p = 0.039) plasma levels. Only for H-FABP (p = 0.069), no significant differences were discernible between the two groups. In addition, cut-off values were calculated to predict an sPAP 40 mmHg. Significant results were shown with 16045.84 pg/mL for sST2 (p = 0.010), with 1117.54 pg/mL for GDF-15 (p = 0.005), with 107028.43 pg/mL for IGF-BP2 (p = 0.029), with 3782.84 pg/mL for suPAR (p = 0.018), with 2248.00 pg/mL for BNP (p 0.001) and with 20.50 pg/mL for cTnI (p = 0.002).
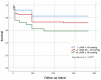
Conclusions: sPAP as an echocardiographic parameter in combination with supplementary use of cardiovascular biomarkers presented here have the potential to provide more detailed information about the presence or absence of PH in a non-invasive way.
Keywords: aortic valve stenosis; biomarker; pulmonary hypertension; systolic pulmonary artery pressure.
Copyright: © 2022 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Michael Lichtenauer is serving as one of the Guest editors of this journal. We declare that Michael Lichtenauer had no involvement in the peer review of this article and has no access to information regarding its peer review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to Dinesh Kalra.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Story of PA/BSA and Biomarkers to Diagnose Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis-The Rise of IGF-BP2 and GDF-15.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Jan 5;10(1):22. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10010022. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 36661917 Free PMC article.
-
Main pulmonary artery diameter in combination with cardiovascular biomarkers: new possibilities to identify pulmonary hypertension in patients with severe aortic valve stenosis.Minerva Med. 2023 Dec;114(6):802-814. doi: 10.23736/S0026-4806.22.08167-8. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Minerva Med. 2023. PMID: 35822856
-
CT measured pulmonary artery to ascending aorta ratio stratified by echocardiographically obtained systolic pulmonary artery pressure values for noninvasive detection of pulmonary hypertension in patients with severe aortic valve stenosis.Clin Res Cardiol. 2023 Oct;112(10):1394-1416. doi: 10.1007/s00392-023-02182-8. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Clin Res Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36935421 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis and Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Non-Invasive Ways of Risk Stratification, Especially in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement.J Pers Med. 2022 Apr 8;12(4):603. doi: 10.3390/jpm12040603. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35455719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of TAPSE/sPAP ratio in predicting pulmonary hypertension and mortality in the systemic sclerosis EUSTAR cohort.Autoimmun Rev. 2023 Apr;22(4):103290. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103290. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Autoimmun Rev. 2023. PMID: 36746368 Review.
Cited by
-
A Story of PA/BSA and Biomarkers to Diagnose Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis-The Rise of IGF-BP2 and GDF-15.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Jan 5;10(1):22. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10010022. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 36661917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Sullivan CJ, Wenaweser P, Ceylan O, Rat-Wirtzler J, Stortecky S, Heg D, et al. Effect of Pulmonary Hypertension Hemodynamic Presentation on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Severe Symptomatic Aortic Valve Stenosis Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions . 2015;8:e002358. - PubMed
-
- Weber L, Rickli H, Haager PK, Joerg L, Weilenmann D, Brenner R, et al. Haemodynamic mechanisms and long-term prognostic impact of pulmonary hypertension in patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing valve replacement. European Journal of Heart Failure . 2019;21:172–181. - PubMed
-
- Schewel J, Schmidt T, Kuck K, Frerker C, Schewel D. Impact of Pulmonary Hypertension Hemodynamic Status on Long-Term Outcome after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions . 2019;12:2155–2168. - PubMed
-
- Sultan I, Fukui M, Bianco V, Brown JA, Kliner DE, Hickey G, et al. Impact of Combined Pre and Postcapillary Pulmonary Hypertension on Survival after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. The American Journal of Cardiology . 2020;131:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. European Heart Journal . 2016;37:67–119. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

