Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio associated with 28-day all-cause mortality in septic patients with coronary artery disease: a retrospective analysis of MIMIC-IV database
- PMID: 39075364
- PMCID: PMC11288105
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09516-5
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio associated with 28-day all-cause mortality in septic patients with coronary artery disease: a retrospective analysis of MIMIC-IV database
Abstract
Background: High Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR), Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) were associated with worse prognosis of patients with sepsis. In-hospital mortality has been reported to be higher in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and sepsis than those with sepsis alone. However, the relationship between NLR, MLR, PLR and mortality in septic patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) remains unclear. The study aimed to explore the association between NLR, MLR, PLR and 28-day all-cause mortality in septic patients with CAD.
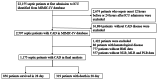
Methods: We performed an observational cohort study of septic patients with CAD from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC)-IV database between 2008 and 2019. The patients were categorized by three group (Q1: low levels, Q2: medium levels, Q3: high levels) based on tertiles of NLR, MLR, and PLR. The associations between NLR, MLR, PLR and 28-day all-cause mortality were examined using the Cox proportional hazards model. Subsequently, we applied receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis for predicting 28-day mortality in septic patients with CAD by combining NLR, MLR and PLR with the modified sequential organ failure assessment (mSOFA) scores.
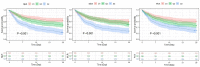
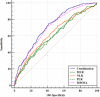
Results: Overall 1,175 septic patients with CAD were included in the study. Observed all-cause mortality rates in 28 days were 27.1%. Multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis results showed that 28-day all-cause mortality of septic patients with CAD was significantly related to rising NLR levels (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR]: 1.02; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.01-1.02; P < 0.001), MLR levels (aHR: 1.29; 95%CI: 1.18-1.41; P < 0.001), and PLR levels (aHR: 1.0007; 95%CI: 1.0004-1.0011; P < 0.001). Meanwhile, the higher levels (Q3) group of NLR, MLR, and PLR also had a higher risk of 28-day all-cause mortality than the lower (Q1) group. The area under the ROC curve of NLR, MLR, PLR, and mSOFA score were 0.630 (95%CI 0.595-0.665), 0.611 (95%CI 0.576-0.646), 0.601 (95%CI 0.567-0.636) and 0.718 (95%CI 0.689-0.748), respectively. Combining NLR, MLR, and PLR with mSOFA scores may improve ability of predicting 28-day mortality (AUC: 0.737, 95%CI 0.709-0.766).
Conclusion: Higher levels of NLR, MLR and PLR were associated with 28-day all-cause mortality in septic patients with CAD. Further investigation will be needed to improve understanding of the pathophysiology of this relationship.
Keywords: Biomarker; Coronary artery disease; Sepsis; Sequential organ failure assessment scores.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this study have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) as Biomarkers in Diagnosis Evaluation of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Retrospective, Observational Study.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024 Apr 15;19:933-943. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S452444. eCollection 2024. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024. PMID: 38646605 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio and monocyte-lymphocyte ratio: a superior prognostic factor of endometrial cancer.BMC Cancer. 2020 May 24;20(1):464. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06953-8. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32448185 Free PMC article.
-
NLR, MLR, and PLR are adverse prognostic variables for sleeve lobectomy within non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2024 Aug;15(24):1792-1804. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15405. Epub 2024 Jul 21. Thorac Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39034535 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, platelet to lymphocyte ratio, and monocyte to lymphocyte ratio in depression: A meta-analysis.J Affect Disord. 2022 Jul 1;308:375-383. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.04.038. Epub 2022 Apr 16. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 35439466 Review.
-
Associations of novel complete blood count-derived inflammatory markers with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 May 24;316(6):228. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-02994-2. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38787437 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical characteristics and prognosis analysis of pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infection in adults: a retrospective study.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Nov 13;25(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01517-7. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39535677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Machado FR, Cavalcanti AB, Bozza FA, Ferreira EM, Angotti Carrara FS, Sousa JL, Caixeta N, Salomao R, Angus DC, Pontes Azevedo LC. The epidemiology of sepsis in Brazilian intensive care units (the Sepsis PREvalence Assessment Database, SPREAD): an observational study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:1180–9. 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30322-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

