The story of clobenpropit and CXCR4: can be an effective drug in cancer and autoimmune diseases?
- PMID: 39070795
- PMCID: PMC11272485
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1410104
The story of clobenpropit and CXCR4: can be an effective drug in cancer and autoimmune diseases?
Abstract
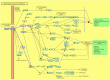
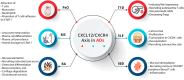
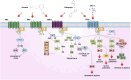
Clobenpropit is a histamine H3 receptor antagonist and has developed as a potential therapeutic drug due to its ability to inhibit CXCR4, a chemokine receptor involved in autoimmune diseases and cancer pathogenesis. The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis involves several biological phenomena, including cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, inflammation, and metastasis. Accordingly, inhibiting CXCR4 can have promising clinical outcomes in patients with malignancy or autoimmune disorders. Based on available knowledge, Clobenpropit can effectively regulate the release of monocyte-derived inflammatory cytokine in autoimmune diseases such as juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), presenting a potential targeted target with possible advantages over current therapeutic approaches. This review summarizes the intricate interplay between Clobenpropit and CXCR4 and the molecular mechanisms underlying their interactions, comprehensively analyzing their impact on immune regulation. Furthermore, we discuss preclinical and clinical investigations highlighting the probable efficacy of Clobenpropit for managing autoimmune diseases and cancer. Through this study, we aim to clarify the immunomodulatory role of Clobenpropit and its advantages and disadvantages as a novel therapeutic opportunity.
Keywords: CXCL12 (SDF-1α); CXCR4; autoimmune disease; cancer; clobenpropit.
Copyright © 2024 Abbasifard, Bagherzadeh and Khorramdelazad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting the chemokine receptor CXCR4 with histamine analog to reduce inflammation in juvenile arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 26;14:1178172. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1178172. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37822935 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL12/CXCR4 signal transduction in diseases and its molecular approaches in targeted-therapy.Immunol Lett. 2020 Jan;217:91-115. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.11.007. Epub 2019 Nov 17. Immunol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31747563 Review.
-
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist inhibits matastatic potential by down-regulating CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling axis in colorectal cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Dec 20;19(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00804-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34930323 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL12/SDF-1α induces migration via SRC-mediated CXCR4-EGFR cross-talk in gastric cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2017 Aug;14(2):2103-2110. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6389. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28781651 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL12-CXCR4 axis in angiogenesis, metastasis and stem cell mobilization.Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(35):3903-20. doi: 10.2174/138161210794455003. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 21158728 Review.
References
-
- Abbasifard M., Fakhrabadi A. H., Bahremand F., Khorramdelazad H. (2023). Evaluation of the interaction between tumor growth factor-β and interferon type I pathways in patients with COVID-19: focusing on ages 1 to 90 years. BMC Infect. Dis. 23 (1), 248. 10.1186/s12879-023-08225-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abbasifard M., Kamiab Z., Hasani M., Rahnama A., Saeed-Askari P., Khorramdelazad H. (2020). Assessing the expression of immunosuppressive cytokines in the newly diagnosed systemic lupus Erythematosus patients: a focus on B cells. Bmc Immunol. 21 (1), 58–12. 10.1186/s12865-020-00388-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdelaal N. H., Elhefnawy N. G., Abdulmonem S. R., Sayed S., Saleh N. A., Saleh M. A. (2020). Evaluation of the expression of the stromal cell‐derived factor‐1 alpha (CXCL 12) in psoriatic patients after treatment with Methotrexate. J. Cosmet. Dermatology 19 (1), 253–258. 10.1111/jocd.12994 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

