This is a preprint.
Comparison of the Amyloid Plaque Proteome in Down Syndrome, Early-Onset Alzheimer's Disease and Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 39070643
- PMCID: PMC11275979
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4469045/v1
Comparison of the Amyloid Plaque Proteome in Down Syndrome, Early-Onset Alzheimer's Disease and Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease
Update in
-
Comparison of the amyloid plaque proteome in Down syndrome, early-onset Alzheimer's disease, and late-onset Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2025 Jan 18;149(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s00401-025-02844-z. Acta Neuropathol. 2025. PMID: 39825890 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Down syndrome (DS) is strongly associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD), attributable to APP overexpression. DS exhibits Amyloid-β (Aβ) and Tau pathology similar to early-onset AD (EOAD) and late-onset AD (LOAD). The study aimed to evaluate the Aβ plaque proteome of DS, EOAD and LOAD.
Methods: Using unbiased localized proteomics, we analyzed amyloid plaques and adjacent plaque-devoid tissue ('non-plaque') from post-mortem paraffin-embedded tissues in four cohorts (n = 20/group): DS (59.8 ± 4.99 y/o), EOAD (63 ± 4.07 y/o), LOAD (82.1 ± 6.37 y/o) and controls (66.4 ± 13.04). We assessed functional associations using Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment and protein interaction networks.
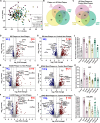
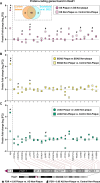
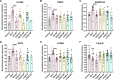
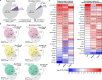
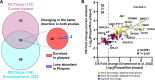
Results: We identified differentially abundant Aβ plaque proteins vs. non-plaques (FDR < 5%, fold-change > 1.5) in DS (n = 132), EOAD (n = 192) and in LOAD (n = 128); there were 43 plaque-associated proteins shared between all groups. Positive correlations (p < 0.0001) were observed between plaque-associated proteins in DS and EOAD (R2 = 0.77), DS and LOAD (R2 = 0.73), and EOAD vs. LOAD (R2 = 0.67). Top Biological process (BP) GO terms (p < 0.0001) included lysosomal transport for DS, immune system regulation for EOAD, and lysosome organization for LOAD. Protein networks revealed a plaque enriched signature across all cohorts involving APP metabolism, immune response, and lysosomal functions. In DS, EOAD and LOAD non-plaque vs. control tissue, we identified 263, 269, and 301 differentially abundant proteins, including 65 altered non-plaque proteins across all cohorts. Differentially abundant non-plaque proteins in DS showed a significant (p < 0.0001) but weaker positive correlation with EOAD (R2 = 0.59) and LOAD (R2 = 0.33) compared to the stronger correlation between EOAD and LOAD (R2 = 0.79). The top BP GO term for all groups was chromatin remodeling (DS p = 0.0013, EOAD p = 5.79×10- 9, and LOAD p = 1.69×10- 10). Additional GO terms for DS included extracellular matrix (p = 0.0068), while EOAD and LOAD were associated with protein-DNA complexes and gene expression regulation (p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: We found strong similarities among the Aβ plaque proteomes in individuals with DS, EOAD and LOAD, and a robust association between the plaque proteomes and lysosomal and immune-related pathways. Further, non-plaque proteomes highlighted altered pathways related to chromatin structure and extracellular matrix (ECM), the latter particularly associated with DS. We identified novel Aβ plaque proteins, which may serve as biomarkers or therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid-β; Down syndrome; Neuropathology; Proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests OD have equity in Regel Therapeutics and Tevard Biosciences. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of the amyloid plaque proteome in Down syndrome, early-onset Alzheimer's disease, and late-onset Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2025 Jan 18;149(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s00401-025-02844-z. Acta Neuropathol. 2025. PMID: 39825890 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum: Eyestalk Ablation to Increase Ovarian Maturation in Mud Crabs.J Vis Exp. 2023 May 26;(195). doi: 10.3791/6561. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37235796
-
Amyloid-β peptide signature associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy in familial Alzheimer's disease with APPdup and Down syndrome.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Jul 18;148(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02756-4. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 39026031 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conservative, physical and surgical interventions for managing faecal incontinence and constipation in adults with central neurological diseases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 29;10(10):CD002115. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002115.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39470206
References
-
- de Graaf G, Buckley F, Skotko BG. Estimation of the number of people with Down syndrome in the United States. Genet Med. 2017;19(4):439–47. - PubMed
-
- Glenner GG, Wong CW. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984;120(3):885–90. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

