Biosimilars in the Era of Artificial Intelligence-International Regulations and the Use in Oncological Treatments
- PMID: 39065775
- PMCID: PMC11279612
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17070925
Biosimilars in the Era of Artificial Intelligence-International Regulations and the Use in Oncological Treatments
Abstract
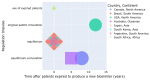
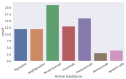
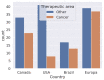
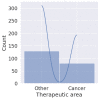
This research is based on three fundamental aspects of successful biosimilar development in the challenging biopharmaceutical market. First, biosimilar regulations in eight selected countries: Japan, South Korea, the United States, Canada, Brazil, Argentina, Australia, and South Africa, represent the four continents. The regulatory aspects of the countries studied are analyzed, highlighting the challenges facing biosimilars, including their complex approval processes and the need for standardized regulatory guidelines. There is an inconsistency depending on whether the biosimilar is used in a developed or developing country. In the countries observed, biosimilars are considered excellent alternatives to patent-protected biological products for the treatment of chronic diseases. In the second aspect addressed, various analytical AI modeling methods (such as machine learning tools, reinforcement learning, supervised, unsupervised, and deep learning tools) were analyzed to observe patterns that lead to the prevalence of biosimilars used in cancer to model the behaviors of the most prominent active compounds with spectroscopy. Finally, an analysis of the use of active compounds of biosimilars used in cancer and approved by the FDA and EMA was proposed.
Keywords: EMA; FDA; artificial intelligence; biosimilars; cancer; continents; oncology; regulations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Improving oncology biosimilar launches in the EU, the USA, and Japan: an updated Policy Review from the Southern Network on Adverse Reactions.Lancet Oncol. 2020 Dec;21(12):e575-e588. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30485-X. Lancet Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33271114 Review.
-
Biosimilars for the next decade in Latin America: a window of opportunity.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2023 Jul-Dec;23(8):659-669. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2023.2245780. Epub 2023 Aug 8. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37542714
-
The regulatory landscape of biosimilars: Algeria's efforts and progress made from 2006 to 2021.Ann Pharm Fr. 2022 Jul;80(4):440-447. doi: 10.1016/j.pharma.2021.11.002. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Ann Pharm Fr. 2022. PMID: 34767827
-
The Biosimilar Landscape: An Overview of Regulatory Approvals by the EMA and FDA.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Dec 31;13(1):48. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13010048. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33396369 Free PMC article.
-
Biosimilars in Developed and Developing East and Southeast Asian Countries: Japan, South Korea, and Malaysia-Overview, Evolution, and Regulations Assessment.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:5910403. doi: 10.1155/2016/5910403. Epub 2016 Apr 24. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27213153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Conlé M. Recent developments in China’s biopharmaceutical industry (2012–2017): Patterns of product innovation and firm scope. J. Sci. Technol. Policy Manag. 2019;10:686–707. doi: 10.1108/JSTPM-11-2018-0106. - DOI
-
- Rose S.A., Rice T. The Biosimilar Action Plan: An Effective Mechanism for Balancing Biologic Innovation and Competition in the United States? (18 November 2019). McGeorge Law Review, Forthcoming, Wake Forest Univ. Legal Studies Paper. [(accessed on 15 May 2024)]. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3489444. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

