Selaginella tamariscina Ethanol Extract Attenuates Influenza A Virus Infection by Inhibiting Hemagglutinin and Neuraminidase
- PMID: 39064820
- PMCID: PMC11280371
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16142377
Selaginella tamariscina Ethanol Extract Attenuates Influenza A Virus Infection by Inhibiting Hemagglutinin and Neuraminidase
Abstract
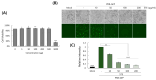
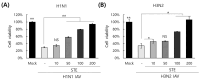
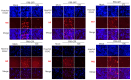
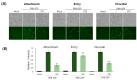
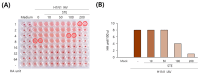
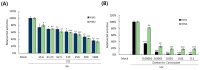
Selaginella tamariscina is a perennial plant that is used for diverse diseases. This study investigated whether Selaginella tamariscina has an antiviral effect against influenza A virus (IAV) infection. We used green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged influenza A virus (IAV) to examine the effect of Selaginella tamariscina ethanol extract (STE) on influenza viral infection. Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry showed that STE potently represses GFP expression by the virus, dose-dependently. STE significantly inhibited the expression of the IAV M2, NP, HA, NA, NS1, and PB2 proteins. Time-of-addition and hemagglutination inhibition assays showed that STE has an inhibitory effect on hemagglutinin and viral binding on the cells at an early infection time. In addition, STE exerted a suppressive effect on the neuraminidase activity of the H1N1 and H3N2 IAVs. Furthermore, dose-dependently, STE inhibited the cytopathic effect induced by H3N2, as well as by H1N1 IAV. Especially in the presence of 200 µg/mL STE, the cytopathic effect was completely blocked. Our findings suggest that STE has antiviral efficacy against IAV infection; thus, it could be developed as a natural IAV inhibitor.
Keywords: Selaginella tamariscina; cytopathic effect; hemagglutinin; influenza A virus; neuraminidase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiviral Effect of Isoquercitrin against Influenza A Viral Infection via Modulating Hemagglutinin and Neuraminidase.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 28;23(21):13112. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113112. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361900 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral activity of furanocoumarins isolated from Angelica dahurica against influenza a viruses H1N1 and H9N2.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Sep 15;259:112945. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112945. Epub 2020 May 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32389854
-
The antiviral activity of Thuja orientalis folium against Influenza A virus.Virus Res. 2023 Oct 2;335:199199. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199199. Epub 2023 Aug 20. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 37582473 Free PMC article.
-
The traditional and modern uses of Selaginella tamariscina (P.Beauv.) Spring, in medicine and cosmetic: Applications and bioactive ingredients.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Nov 15;280:114444. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114444. Epub 2021 Jul 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34302944 Review.
-
Effect of natural products on host cell autophagy induced by Influenza A virus infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 30;14:1460604. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1460604. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39403204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Atkins N., Harikar M., Duggan K., Zawiejska A., Vardhan V., Vokey L., Dozier M., de Los Godos E.F., McSwiggan E., McQuillan R., et al. What are the characteristics of participatory surveillance systems for influenza-like-illness? J. Glob. Health. 2023;13:04130. doi: 10.7189/jogh.13.04130. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

