Astragalus Extract Mixture HT042 Alleviates Dexamethasone-Induced Bone Growth Retardation in Rat Metatarsal Bones
- PMID: 39064775
- PMCID: PMC11279921
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16142333
Astragalus Extract Mixture HT042 Alleviates Dexamethasone-Induced Bone Growth Retardation in Rat Metatarsal Bones
Abstract
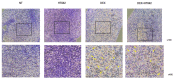
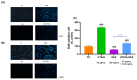
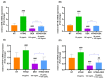
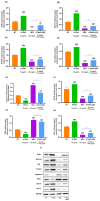
The most widely used synthetic glucocorticoid, dexamethasone (DEX), causes stunted growth in children when used excessively or for long periods of time; however, there are still plenty of pediatric patients require long-term treatment with DEX. As an alternative, growth hormone is used in combination, but it has side effects, a high cost, and psychological factors, and it is not satisfactory in terms of effectiveness. It is necessary to develop a safe and affordable treatment that can replace it. The Korean Food and Drug Administration approved HT042, a standardized functional food ingredient, with the claim that it can help height growth of children. In this study, it was found that HT042 activated the Indian hedgehog/parathyroid hormone-related protein signaling pathway and enhanced the number of growth hormone receptors and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors on the growth plate surface, which were reduced by DEX treatment, and restored growth retardation. In metatarsal bone and primary chondrocyte models, it was found that HT042 can promote the length of growth plate and recover DEX-induced growth retardation. It was also found that HT042 promotes cell proliferation using bromodeoxyuridine and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling assays; moreover, we verified increased expression of GHR/IGF-1R and Ihh/PTHrP pathway activity using qRT-PCR, western blotting, and siRNA analyses to verify its direct action on the growth plate. The anti-apoptotic effect of HT042 was identified by regulating the expression of apoptotic factors such as caspase-3, Bcl2, Bclx, and Bax. These results were identified using both ex vivo and in vitro models. Our study verified that co-administration of HT042 could recover the DEX induced growth retardation.
Keywords: HT042; apoptosis; dexamethasone; growth retardation; hypertrophy; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this publication. In addition, there is no significant financial support affecting the outcome of this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Skeletal growth and IGF levels in rats after HT042 treatment.Phytother Res. 2012 Dec;26(12):1771-8. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4642. Epub 2012 Mar 3. Phytother Res. 2012. PMID: 22388791
-
IGF-1R signaling in chondrocytes modulates growth plate development by interacting with the PTHrP/Ihh pathway.J Bone Miner Res. 2011 Jul;26(7):1437-46. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.359. J Bone Miner Res. 2011. PMID: 21312270 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous growth hormone functionally alleviates glucocorticoid-induced longitudinal bone growth retardation in male rats by activating the Ihh/PTHrP signaling pathway.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2022 Apr 5;545:111571. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2022.111571. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35063477
-
The herbal formula HT042 induces longitudinal bone growth in adolescent female rats.J Med Food. 2010 Dec;13(6):1376-84. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2010.1007. J Med Food. 2010. PMID: 21091251
-
Indian hedgehog: its roles and regulation in endochondral bone development.J Cell Biochem. 2005 Dec 15;96(6):1163-73. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20635. J Cell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16187314 Review.
References
-
- Wong S.C., Dobie R., Altowati M.A., Werther G.A., Farquharson C., Ahmed S.F. Growth and the Growth Hormone-Insulin Like Growth Factor 1 Axis in Children With Chronic Inflammation: Current Evidence, Gaps in Knowledge, and Future Directions. Endocr. Rev. 2016;37:62–110. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1026. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

