The Role of Neutrophyl-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Ovarian Torsion in Children: Results of a Multicentric Study
- PMID: 39063642
- PMCID: PMC11277755
- DOI: 10.3390/life14070889
The Role of Neutrophyl-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Ovarian Torsion in Children: Results of a Multicentric Study
Abstract
Introduction: Pediatric ovarian torsion (OT) is an emergency condition that remains challenging to diagnose because of its overall unspecific clinical presentation. The aim of this study was to determine the diagnostic value of clinical, ultrasound, and inflammatory laboratory markers in pediatric OT.
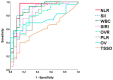
Methods: We performed a retrospective multicentric case-control study in patients with clinical and ultrasound suspicion of OT, in whom surgical examination was performed between 2016-2022 in seven pediatric hospitals. Patients were divided into two groups according to intraoperative findings: OT group (ovarian torsion), defined as torsion of the ovarian axis at least 360°, and non-OT group (no torsion). Demographics, clinical, ultrasound, and laboratory features at admission were analyzed. The diagnostic yield analysis was performed using logistic regression models, and the results were represented by ROC curves.
Results: We included a total of 110 patients (75 in OT group; 35 in non-OT group), with no demographic or clinical differences between them. OT-group patients had shorter time from symptom onset (8 vs. 12 h; p = 0.023), higher ultrasound median ovarian volume (63 vs. 51 mL; p = 0.013), and a significant increase in inflammatory markers (leukocytes, neutrophils, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, C-reactive protein) when compared to the non-OT group. In the ROC curve analysis, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) presented the highest AUC (0.918), with maximum sensitivity (92.4%) and specificity (90.1%) at the cut-off point NLR = 2.57.
Conclusions: NLR can be considered as a useful predictor of pediatric OT in cases with clinical and ultrasound suspicion. Values above 2.57 may help to anticipate urgent surgical treatment in these patients.
Keywords: children; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; ovarian torsion; predictive factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of testicular torsion in children.J Pediatr Urol. 2022 Oct;18(5):697.e1-697.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2022.09.010. Epub 2022 Sep 14. J Pediatr Urol. 2022. PMID: 36175289
-
Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio Might Predict Pediatric Ovarian Torsion: A Single-Institution Experience and Review of the Literature.J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2021 Jun;34(3):334-340. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2020.12.003. Epub 2020 Dec 13. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33316415
-
Key clinical predictors in the diagnosis of ovarian torsion in children.J Pediatr (Rio J). 2024 Jul-Aug;100(4):399-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2024.01.006. Epub 2024 Apr 3. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2024. PMID: 38582497 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Ovarian Torsion: Should You Go With the Flow?Pediatr Emerg Care. 2022 Jun 1;38(6):e1332-e1335. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000002679. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2022. PMID: 35639437 Review.
-
Ovarian torsion in the pediatric population: predictive factors for ovarian-sparing surgery-an international retrospective multicenter study and a systematic review.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023 Jul;308(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06522-3. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023. PMID: 35751675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

