Evaluation of a New Closed-System Automated RT-qPCR Assay for the Rapid Detection and Monitoring of Common Nucleophosmin Mutations in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 39063154
- PMCID: PMC11277538
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25147912
Evaluation of a New Closed-System Automated RT-qPCR Assay for the Rapid Detection and Monitoring of Common Nucleophosmin Mutations in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
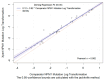
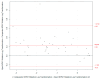
Quantitative assessment of nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) mutation status is integral to evaluating measurable residual disease (MRD) in NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. In a retrospective study, leftover peripheral blood (PB) specimens (n = 40) which were collected for routine clinical diagnostic evaluations of AML disease burden were tested by both a novel automated RT-qPCR quantitative NPM1 assay (Xpert NPM1 mutation assay) and the NPM1 mutA, mutB&D MutaQuant kit. Based on a Deming regression analysis, there was a high correlation (slope = 0.92; intercept = 0.12; Pearson's r = 0.982) between the quantitative results of the Xpert NPM1 mutation assay and the NPM1 mutA, mutB&D MutaQuant kit. The Xpert test quantitative results are thus highly correlated with the comparator method and the former has potential as a useful alternative for the monitoring of AML patients with a known NPM1 mutation.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; minimal residual disease (MRD); monitoring; nucleophosmin (NPM1) mutation; polymerase chain reaction.
Conflict of interest statement
R.D.P. has consulted for Cepheid; M.M. received honoraria and speaker’s fees from Cepheid; Authors A.R., R.R.D., and R.K. were employed by Cepheid. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measurable residual disease detected by flow cytometry independently predicts prognoses of NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia.Ann Hematol. 2023 Feb;102(2):337-347. doi: 10.1007/s00277-022-05033-0. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Ann Hematol. 2023. PMID: 36378304
-
An allele-specific rt-PCR assay to detect type A mutation of the nucleophosmin-1 gene in acute myeloid leukemia.J Mol Diagn. 2008 May;10(3):212-6. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2008.070166. Epub 2008 Apr 10. J Mol Diagn. 2008. PMID: 18403613 Free PMC article.
-
Minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia by mutant nucleophosmin (NPM1): comparison with WT1 gene expression.Clin Chim Acta. 2008 Sep;395(1-2):120-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2008.05.021. Epub 2008 Jun 8. Clin Chim Acta. 2008. PMID: 18590714
-
Minimal/Measurable Residual Disease Monitoring in NPM1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Clinical Viewpoint and Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 6;19(11):3492. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113492. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30404199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting and Monitoring Acute Myeloid Leukaemia with Nucleophosmin-1 (NPM1) Mutation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 5;24(4):3161. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043161. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia—Cancer Stat Facts. National Cancer Institute—Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. [(accessed on 23 February 2024)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html.
-
- Coleman W.B. Molecular Testing in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. In: Coleman W.B., Tsongalis G.J., editors. Diagnostic Molecular Pathology—A Guide to Applied Molecular Testing. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2016.
-
- Pollyea D.A., Altman J.K., Assi R., Bixby D., Fathi A.T., Foran J.M., Gojo I., Hall A.C., Jonas B.A., Kishtagari A., et al. Acute myeloid leukemia, version 3.2023, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2023;21:503–513. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2023.0025. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

