Chemokine CX3CL1 (Fractalkine) Signaling and Diabetic Encephalopathy
- PMID: 39062768
- PMCID: PMC11277241
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25147527
Chemokine CX3CL1 (Fractalkine) Signaling and Diabetic Encephalopathy
Abstract
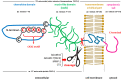
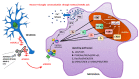
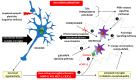
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is the most common metabolic disease in humans, and its prevalence is increasing worldwide in parallel with the obesity pandemic. A lack of insulin or insulin resistance, and consequently hyperglycemia, leads to many systemic disorders, among which diabetic encephalopathy (DE) is a long-term complication of the central nervous system (CNS), characterized by cognitive impairment and motor dysfunctions. The role of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in the pathomechanism of DE has been proven. Fractalkine (CX3CL1) has unique properties as an adhesion molecule and chemoattractant, and by acting on its only receptor, CX3CR1, it regulates the activity of microglia in physiological states and neuroinflammation. Depending on the clinical context, CX3CL1-CX3CR1 signaling may have neuroprotective effects by inhibiting the inflammatory process in microglia or, conversely, maintaining/intensifying inflammation and neurotoxicity. This review discusses the evidence supporting that the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 pair is neuroprotective and other evidence that it is neurotoxic. Therefore, interrupting the vicious cycle within neuron-microglia interactions by promoting neuroprotective effects or inhibiting the neurotoxic effects of the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 signaling axis may be a therapeutic goal in DE by limiting the inflammatory response. However, the optimal approach to prevent DE is simply tight glycemic control, because the elimination of dysglycemic states in the CNS abolishes the fundamental mechanisms that induce this vicious cycle.
Keywords: CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis; advanced glycation end products; central nervous system; chemokine CX3CL1; diabetes mellitus; diabetic encephalopathy; fractalkine; hyperglycemia; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fractalkine/CX3CR1 is involved in the cross-talk between neuron and glia in neurological diseases.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Mar;146:12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.11.017. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30496784 Review.
-
The Impact of the CX3CL1/CX3CR1 Axis in Neurological Disorders.Cells. 2020 Oct 13;9(10):2277. doi: 10.3390/cells9102277. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33065974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the Role of CX3CL1 (Fractalkine) and Its Receptor CX3CR1 in Traumatic Brain and Spinal Cord Injury: Insight into Recent Advances in Actions of Neurochemokine Agents.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Apr;54(3):2167-2188. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9787-4. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26927660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signaling targets for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Mar;231:107989. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107989. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34492237 Review.
-
Evidence for a protective role of the CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis in a model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 24;400(5):651-661. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2018-0204. Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30352020
References
-
- Kibirige D., Chamba N., Andia-Biraro I., Kilonzo K., Laizer S.N., Sekitoleko I., Kyazze A.P., Ninsiima S., Ssekamatte P., Bongomin F., et al. Indicators of optimal diabetes care and burden of diabetes complications in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e060786. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-060786. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

