Roles of Lysine Methylation in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: Functions, Regulatory Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 39062577
- PMCID: PMC11274642
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14070862
Roles of Lysine Methylation in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: Functions, Regulatory Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
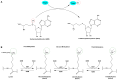
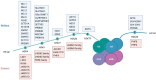
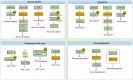
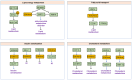
Glucose and lipid metabolism are essential energy sources for the body. Dysregulation in these metabolic pathways is a significant risk factor for numerous acute and chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes (T2DM), Alzheimer's disease (AD), obesity, and cancer. Post-translational modifications (PTMs), which regulate protein structure, localization, function, and activity, play a crucial role in managing cellular glucose and lipid metabolism. Among these PTMs, lysine methylation stands out as a key dynamic modification vital for the epigenetic regulation of gene transcription. Emerging evidence indicates that lysine methylation significantly impacts glucose and lipid metabolism by modifying key enzymes and proteins. This review summarizes the current understanding of lysine methylation's role and regulatory mechanisms in glucose and lipid metabolism. We highlight the involvement of methyltransferases (KMTs) and demethylases (KDMs) in generating abnormal methylation signals affecting these metabolic pathways. Additionally, we discuss the chemical biology and pharmacology of KMT and KDM inhibitors and targeted protein degraders, emphasizing their clinical implications for diseases such as diabetes, obesity, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancers. This review suggests that targeting lysine methylation in glucose and lipid metabolism could be an ideal therapeutic strategy for treating these diseases.
Keywords: glucose metabolism; lipid metabolism; lysine methylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Roles of protein post-translational modifications in glucose and lipid metabolism: mechanisms and perspectives.Mol Med. 2023 Jul 6;29(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00684-9. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37415097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical biology and pharmacology of histone lysine methylation inhibitors.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2022 Aug;1865(6):194840. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2022.194840. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2022. PMID: 35753676 Review.
-
Lysine methylation: Implications in neurodegenerative disease.Brain Res. 2019 Mar 15;1707:164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.11.024. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30465751 Review.
-
Tipping the lysine methylation balance in disease.Biopolymers. 2013 Feb;99(2):127-35. doi: 10.1002/bip.22136. Biopolymers. 2013. PMID: 23175387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysine Methyltransferases Signaling: Histones are Just the Tip of the Iceberg.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(7):655-674. doi: 10.2174/1871527319666200102101608. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020. PMID: 31894745 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone methylation modification and diabetic kidney disease: Potential molecular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Nov;54(5):104. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5428. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39301658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

