Treating Cardiovascular Disease in the Inflammatory Setting of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Ongoing Challenge
- PMID: 39062180
- PMCID: PMC11275112
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12071608
Treating Cardiovascular Disease in the Inflammatory Setting of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Ongoing Challenge
Abstract
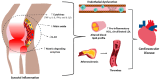
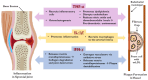
Despite progress in treating rheumatoid arthritis, this autoimmune disorder confers an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD). Widely used screening protocols and current clinical guidelines are inadequate for the early detection of CVD in persons with rheumatoid arthritis. Traditional CVD risk factors alone cannot be applied because they underestimate CVD risk in rheumatoid arthritis, missing the window of opportunity for prompt intervention to decrease morbidity and mortality. The lipid profile is insufficient to assess CVD risk. This review delves into the connection between systemic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and the premature onset of CVD. The shared inflammatory and immunologic pathways between the two diseases that result in subclinical atherosclerosis and disrupted cholesterol homeostasis are examined. The treatment armamentarium for rheumatoid arthritis is summarized, with a particular focus on each medication's cardiovascular effect, as well as the mechanism of action, risk-benefit profile, safety, and cost. A clinical approach to CVD screening and treatment for rheumatoid arthritis patients is proposed based on the available evidence. The mortality gap between rheumatoid arthritis and non-rheumatoid arthritis populations due to premature CVD represents an urgent research need in the fields of cardiology and rheumatology. Future research areas, including risk assessment tools and novel immunotherapeutic targets, are highlighted.
Keywords: biological therapy; cardiovascular disease; inflammation; rheumatoid arthritis; statin; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Surrogate Markers of Cardiovascular Risk in the Setting of Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: Current Data and Implications for the Future.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 30;9:820263. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.820263. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35847825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: how to lower the risk?Atherosclerosis. 2013 Nov;231(1):163-72. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.09.006. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Atherosclerosis. 2013. PMID: 24125429 Review.
-
EULAR recommendations for cardiovascular disease risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory joint disorders: 2015/2016 update.Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jan;76(1):17-28. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209775. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 27697765 Review.
-
Practical Management of Cardiovascular Comorbidities in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Rheumatol Ther. 2017 Dec;4(2):293-308. doi: 10.1007/s40744-017-0068-0. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Rheumatol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28752316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The comparison of cardiovascular disease risk prediction scores and evaluation of subclinical atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Dec;41(12):3675-3686. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06349-y. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 36006556
References
-
- Cai Y., Zhang J., Liang J., Xiao M., Zhang G., Jing Z., Lv L., Nan K., Dang X. The Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Findings from the 2019 Global Burden of Diseases Study and Forecasts for 2030 by Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023;12:1291. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041291. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

