Interactions Involving Glycine and Other Amino Acid Neurotransmitters: Focus on Transporter-Mediated Regulation of Release and Glycine-Glutamate Crosstalk
- PMID: 39062091
- PMCID: PMC11275102
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12071518
Interactions Involving Glycine and Other Amino Acid Neurotransmitters: Focus on Transporter-Mediated Regulation of Release and Glycine-Glutamate Crosstalk
Abstract
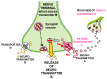
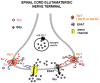
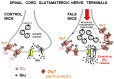
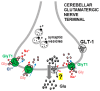
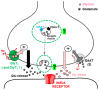
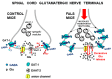
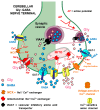
Glycine plays a pivotal role in the Central Nervous System (CNS), being a major inhibitory neurotransmitter as well as a co-agonist of Glutamate at excitatory NMDA receptors. Interactions involving Glycine and other neurotransmitters are the subject of different studies. Functional interactions among neurotransmitters include the modulation of release through release-regulating receptors but also through transporter-mediated mechanisms. Many transporter-mediated interactions involve the amino acid transmitters Glycine, Glutamate, and GABA. Different studies published during the last two decades investigated a number of transporter-mediated interactions in depth involving amino acid transmitters at the nerve terminal level in different CNS areas, providing details of mechanisms involved and suggesting pathophysiological significances. Here, this evidence is reviewed also considering additional recent information available in the literature, with a special (but not exclusive) focus on glycinergic neurotransmission and Glycine-Glutamate interactions. Some possible pharmacological implications, although partly speculative, are also discussed. Dysregulations in glycinergic and glutamatergic transmission are involved in relevant CNS pathologies. Pharmacological interventions on glycinergic targets (including receptors and transporters) are under study to develop novel therapies against serious CNS pathological states including pain, schizophrenia, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative diseases. Although with limitations, it is hoped to possibly contribute to a better understanding of the complex interactions between glycine-mediated neurotransmission and other major amino acid transmitters, also in view of the current interest in potential drugs acting on "glycinergic" targets.
Keywords: GABA; NMDA receptors; glutamate; glycine; glycine transporter 1 (GlyT1); glycine transporter 2 (GlyT2); neurotransmitter release.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interactions between Glycine and Glutamate through Activation of Their Transporters in Hippocampal Nerve Terminals.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 27;11(12):3152. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123152. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137373 Free PMC article.
-
Glycine Transporters and Its Coupling with NMDA Receptors.Adv Neurobiol. 2017;16:55-83. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-55769-4_4. Adv Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28828606 Review.
-
Glycine Signaling in the Framework of Dopamine-Glutamate Interaction and Postsynaptic Density. Implications for Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2020 May 14;11:369. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00369. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32477178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurobiology of glycine transporters: From molecules to behavior.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020 Nov;118:97-110. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.07.025. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020. PMID: 32712279 Review.
-
GlyT1 determines the glycinergic phenotype of amacrine cells in the mouse retina.Brain Struct Funct. 2018 Sep;223(7):3251-3266. doi: 10.1007/s00429-018-1684-3. Epub 2018 May 28. Brain Struct Funct. 2018. PMID: 29808289
Cited by
-
Glycine Transporter 1 Inhibitors Minimize the Analgesic Tolerance to Morphine.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 17;25(20):11136. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011136. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456918 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

