Impaired Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism Regulated by p70S6K: A Putative Pathological Feature in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 39057692
- PMCID: PMC11278668
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo14070369
Impaired Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism Regulated by p70S6K: A Putative Pathological Feature in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
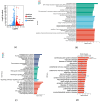
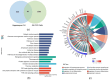
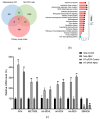
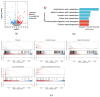
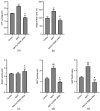
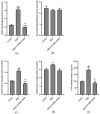
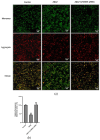
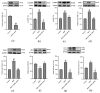
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease. Mitochondrial energy metabolism and p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase (p70S6K) play significant roles in AD pathology. However, the potential relationship between them is unclear. In this study, bioinformatics methods were initially applied to analyze the transcriptomic data in the CA1 and the primary visual cortex of patients with AD and Aβ42-treated SH-SY5Y cells. By applying secreted Aβ42 and p70S6K gene silencing in cells, we explored disorders in mitochondrial function and the regulatory roles of p70S6K by flow cytometry, laser scanning confocal microscopy, high-performance liquid chromatography, Western blotting, and quantitative reverse transcription PCR. The study reveals that impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism is a potential pathological feature of AD and that p70S6K gene silencing reversed most of the changes induced by Aβ42, such as the activities of the electron transport chain complexes I and III, as well as ATP synthase, ATP production, generation of reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial membrane potential, and phosphorylation of AMPK, PINK1, and Parkin, all of which are required for mitochondria to function properly in the cell.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; RNA sequencing; mitochondrial energy metabolism; oxidative phosphorylation; p70S6K; secreted Aβ42.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of zinc-induced phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells.J Neurochem. 2005 Mar;92(5):1104-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02948.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15715661
-
Amyloid β-42 induces neuronal apoptosis by targeting mitochondria.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):4521-4528. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7203. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28849115 Free PMC article.
-
Control of p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase by AMP-activated protein kinase and protein phosphatases in isolated hepatocytes.Eur J Biochem. 2002 Aug;269(15):3751-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03074.x. Eur J Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12153572
-
Mechanisms of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;53(9):6078-6090. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9515-5. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26537901 Review.
-
p70 S6 kinase and tau in Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2008 Aug;14(4):385-92. doi: 10.3233/jad-2008-14405. J Alzheimers Dis. 2008. PMID: 18688088 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

