Hydrogel-Based Therapies for Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 39057499
- PMCID: PMC11276304
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10070476
Hydrogel-Based Therapies for Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
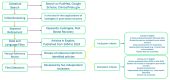
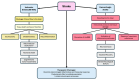
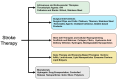
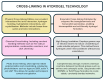
Stroke remains the second leading cause of death and a major cause of disability worldwide, significantly impacting individuals, families, and healthcare systems. This neurological emergency can be triggered by ischemic events, including small vessel arteriolosclerosis, cardioembolism, and large artery atherothromboembolism, as well as hemorrhagic incidents resulting from macrovascular lesions, venous sinus thrombosis, or vascular malformations, leading to significant neuronal damage. The resultant motor impairment, cognitive dysfunction, and emotional disturbances underscore the urgent need for effective therapeutic interventions. Recent advancements in biomaterials, particularly hydrogels, offer promising new avenues for stroke management. Hydrogels, composed of three-dimensional networks of hydrophilic polymers, are notable for their ability to absorb and retain substantial amounts of water. Commonly used polymers in hydrogel formulations include natural polymers like alginate, chitosan, and collagen, as well as synthetic polymers such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and polyacrylamide. Their customizable characteristics-such as their porosity, swelling behavior, mechanical strength, and degradation rates-make hydrogels ideal for biomedical applications, including drug delivery, cell delivery, tissue engineering, and the controlled release of therapeutic agents. This review comprehensively explores hydrogel-based approaches to both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke therapy, elucidating the mechanisms by which hydrogels provide neuroprotection. It covers their application in drug delivery systems, their role in reducing inflammation and secondary injury, and their potential to support neurogenesis and angiogenesis. It also discusses current advancements in hydrogel technology and the significant challenges in translating these innovations from research into clinical practice. Additionally, it emphasizes the limited number of clinical trials utilizing hydrogel therapies for stroke and addresses the associated limitations and constraints, underscoring the need for further research in this field.
Keywords: biomaterials; drug delivery; hydrogels; neuroprotection; stroke; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Harnessing the power of biological macromolecules in hydrogels for controlled drug release in the central nervous system: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jan;254(Pt 1):127708. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127708. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 37923043 Review.
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Novel pH-Responsive Aminated Alginate Derivatives Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering and Drug Delivery.Curr Org Synth. 2023 Nov 3. doi: 10.2174/0115701794210967231016055949. Online ahead of print. Curr Org Synth. 2023. PMID: 37936472
-
Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine.Molecules. 2022 May 2;27(9):2902. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092902. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery Systems.Gels. 2024 Apr 13;10(4):262. doi: 10.3390/gels10040262. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Classification, Properties, Recent Trends, and Applications.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Mar 21;25(4):64. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02786-x. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38514495 Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol Consumption and Cardiovascular Disease: A Narrative Review of Evolving Perspectives and Long-Term Implications.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 9;14(9):1134. doi: 10.3390/life14091134. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337917 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous