Inflammatory Cytokines and Clinical Outcome Following Biological Therapy in Adult Bio-Naïve Psoriasis Patients
- PMID: 39057098
- PMCID: PMC11276069
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46070457
Inflammatory Cytokines and Clinical Outcome Following Biological Therapy in Adult Bio-Naïve Psoriasis Patients
Abstract
Inflammatory cytokines may hold the key to the clinical evolution of psoriasis. The aims of this study are to find a correlation between levels of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-23, IL-17A, and IL-17F and disease duration and severity scores in psoriasis; to test if the decrease in any of the aforementioned cytokines is correlated with an amelioration in disease severity scores; and to analyze if any of the four biologic agents used are linked with a greater decrease in overall cytokine levels. We enrolled 23 adult patients under treatment with ixekizumab, secukinumab, guselkumab, or adalimumab and measured psoriasis disease severity scores PASI (Psoriasis Area Severity Index) and DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index), as well as the levels of the aforementioned cytokines at the start of therapy and after 3 months of continuous treatment. Inclusion criteria were the presence of psoriasis, age above 18 years and the need to initiate biological therapy (lack of response to standard treatment). Biological therapies resulted in an amelioration of PASI and DLQI scores, as well as levels of TNF-α, IL-23 and IL-17F. Disease duration and PASI and DLQI scores did not correlate with cytokine levels except DLQI and IL-23 score, in a paradoxically inversely proportional manner. IL-23, in particular, could be a useful biomarker for checking treatment response in psoriasis.
Keywords: IL-23; biological therapy; inflammatory cytokines; psoriasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
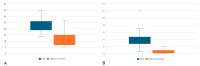
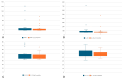
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
-
Brodalumab Seems to Recover Its Therapeutic Efficacy After a Relatively Short "Washout" Period with Anti-TNF Agents: A Successful Pattern for Double-switch Therapy.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2023 Aug;31(1):48-50. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2023. PMID: 37843093
-
Improvement in Patient-Reported Outcomes (Dermatology Life Quality Index and the Psoriasis Symptoms and Signs Diary) with Guselkumab in Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Results from the Phase III VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2 Studies.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019 Feb;20(1):155-164. doi: 10.1007/s40257-018-0396-z. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30417277 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Brodalumab and ixekizumab, anti-interleukin-17-receptor antibodies for psoriasis: a critical appraisal.Br J Dermatol. 2012 Oct;167(4):710-3; discussion 714-5. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12025. Br J Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 23013312
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5(5):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 12;7:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub6. PMID: 35603936 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

