Dietary Chitosan Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Inflammation in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) through Regulation of Nrf2/Kaep1 and Bcl-2/Bax Pathways
- PMID: 39056682
- PMCID: PMC11273726
- DOI: 10.3390/biology13070486
Dietary Chitosan Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Inflammation in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) through Regulation of Nrf2/Kaep1 and Bcl-2/Bax Pathways
Abstract
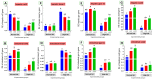
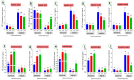
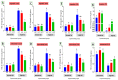
Fatty liver injury is a prevalent condition in most farmed fish, yet the molecular mechanisms underpinning this pathology remain largely elusive. A comprehensive feeding trial spanning eight weeks was conducted to discern the potential of dietary chitosan in mitigating the deleterious effects of a high-fat diet (HFD) while concurrently exploring the underlying mechanism. Growth performance, haemato-biochemical capacity, antioxidant capacity, apoptotic/anti-apoptotic gene expression, inflammatory gene expression, and histopathological changes in the liver, kidney, and intestine were meticulously assessed in Nile tilapia. Six experimental diets were formulated with varying concentrations of chitosan. The first three groups were administered a diet comprising 6% fat with chitosan concentrations of 0%, 5%, and 10% and were designated as F6Ch0, F6Ch5, and F6Ch10, respectively. Conversely, the fourth, fifth, and sixth groups were fed a diet containing 12% fat with chitosan concentrations of 0%, 5%, and 10%, respectively, for 60 days and were termed F12Ch0, F12Ch5, and F12Ch10. The results showed that fish fed an HFD demonstrated enhanced growth rates and a significant accumulation of fat in the perivisceral tissue, accompanied by markedly elevated serum hepatic injury biomarkers and serum lipid levels, along with upregulation of pro-apoptotic and inflammatory markers. In stark contrast, the expression levels of nrf2, sod, gpx, and bcl-2 were notably decreased when compared with the control normal fat group. These observations were accompanied by marked diffuse hepatic steatosis, diffuse tubular damage, and shortened intestinal villi. Intriguingly, chitosan supplementation effectively mitigated the aforementioned findings and alleviated intestinal injury by upregulating the expression of tight junction-related genes. It could be concluded that dietary chitosan alleviates the adverse impacts of an HFD on the liver, kidney, and intestine by modulating the impaired antioxidant defense system, inflammation, and apoptosis through the variation in nrf2 and cox2 signaling pathways.
Keywords: apoptosis; bcl-2/bax; chitosan; high-fat diet; nrf2/kaep1; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
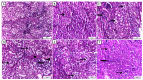

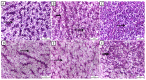
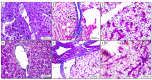
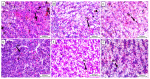
Similar articles
-
Effects of high-fat diet on antioxidative status, apoptosis and inflammation in liver of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) via Nrf2, TLRs and JNK pathways.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020 Sep;104:391-401. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.06.025. Epub 2020 Jun 14. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32553566
-
Potential role of dietary chitosan nanoparticles against immunosuppression, inflammation, oxidative stress, and histopathological alterations induced by pendimethalin toxicity in Nile tilapia.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021 Nov;118:270-282. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2021.09.015. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34537335
-
Synergistic Effects Between Dietary Zinc Form Supplementation and Dietary Protein Levels on Performance, Intestinal Functional Topography, Hemato-biochemical Indices, Immune, Oxidative Response, and Associated Gene Expression of Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022 Jul;200(7):3412-3428. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02911-y. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022. PMID: 34487300
-
High fat diet worsens the adverse effects of antibiotic on intestinal health in juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Sci Total Environ. 2019 Aug 25;680:169-180. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.067. Epub 2019 May 8. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 31103895
-
Immune-antioxidant trait, growth, splenic cytokines expression, apoptosis, and histopathological alterations of Oreochromis niloticus exposed to sub-lethal copper toxicity and fed thyme and/or basil essential oils enriched diets.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022 Dec;131:1006-1018. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.11.013. Epub 2022 Nov 12. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36379445
References
-
- Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) Towards Blue Transformation. Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO); Rome, Italy: 2022. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture.266p. - DOI
-
- Khalil M.T. Achieving Sustainability in the Fishery Sector. Road Map for Green Economy in Egypt. Workshop on 25/6/2014; Academy of Science and Technologies; Cairo, Egypt: 2014.
-
- Cao X.-F., Dai Y.-J., Liu M.-Y., Yuan X.-Y., Wang C.-C., Huang Y.-Y., Liu W.-B., Jiang G.-Z. High-fat diet induces aberrant hepatic lipid secretion in blunt snout bream by activating endoplasmic-reticulum stress-associated IRE1/XBP1 pathway. Biochim. Et. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids. 2019;1864:213–223. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.12.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lu K., Xu W., Li J., Li X., Huang G., Liu W. Alterations of liver histology and blood biochemistry in blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala fed high-fat diets. Fish. Sci. 2013;79:661–671. doi: 10.1007/s12562-013-0635-4. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

