Sporadic Parathyroid Carcinoma Treated With Lenvatinib, Exhibiting a Novel Somatic MEN1 Mutation
- PMID: 39056047
- PMCID: PMC11267463
- DOI: 10.1210/jcemcr/luae121
Sporadic Parathyroid Carcinoma Treated With Lenvatinib, Exhibiting a Novel Somatic MEN1 Mutation
Abstract
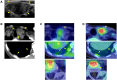
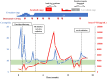
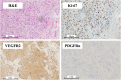
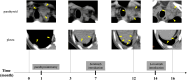
Parathyroid carcinoma (PC) is extremely rare and is primarily treated surgically. Chemotherapy is an option for advanced stages, but no standard regimen exists. Emerging research suggests the efficacy of multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitors (MTKIs) for PC, targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR). A 61-year-old Japanese woman presented with a neck mass, diagnosed as PC with pleural and lumbar metastases. After parathyroidectomy and radiation for lumbar metastasis, immunohistochemistry showed VEGFR overexpression, leading to targeted therapy with MTKIs. Despite no actionable mutations on cancer genomic panel test, a novel MEN1 somatic mutation (NM_130801: exon2: c.332delG: p.G111fs*8) was identified, which may affect VEGFR2 expression and tumor epigenetics. Although severe hand-foot syndrome necessitated dose reductions and treatment interruptions, sorafenib treatment managed hypercalcemia with evocalcet and denosumab. Lenvatinib, as second-line therapy, was effective against pleural metastases but caused thrombocytopenia and hematuria, leading to discontinuation and uncontrolled recurrence and metastasis progression. Our case highlights the need for further research on genomic profiling, molecular targets, and therapy response in PC.
Keywords: MEN1; VEGF receptor; multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitors; parathyroid carcinoma.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Successful Control of Hypercalcemia with Sorafenib, Evocalcet, and Denosumab Combination Therapy for Recurrent Parathyroid Carcinoma.Intern Med. 2022 Nov 15;61(22):3383-3390. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9261-21. Epub 2022 Apr 2. Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35370235 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Profiling of Parathyroid Carcinoma Reveals Genomic Alterations Suggesting Benefit from Therapy.Oncologist. 2019 Jun;24(6):791-797. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0334. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30373905 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of early dose increase of evocalcet for intractable hypercalcemia caused by parathyroid carcinoma.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2023 Jan 5;2023(1):22-0269. doi: 10.1530/EDM-22-0269. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36602916 Free PMC article.
-
Role of anti-angiogenesis agents in treating NSCLC: focus on bevacizumab and VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2007 Feb;8(1):15-27. doi: 10.1007/s11864-007-0022-4. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17634832 Review.
-
Parathyroid carcinoma and atypical parathyroid neoplasms in MEN1 patients; A clinico-pathologic challenge. The MD Anderson case series and review of the literature.Int J Surg. 2016 Jul;31:10-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.05.035. Epub 2016 May 19. Int J Surg. 2016. PMID: 27212590 Review.
Cited by
-
Successful Multimodal Treatment of Locally Advanced Parathyroid Carcinoma.JCEM Case Rep. 2024 Nov 7;2(12):luae208. doi: 10.1210/jcemcr/luae208. eCollection 2024 Dec. JCEM Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39526029 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walker MD, Shane E. Hypercalcemia: a review. JAMA. 2022;328(16):1624‐1636. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
