Targeting Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin-2 (TRPM2) Enhances Therapeutic Efficacy of Third Generation EGFR Inhibitors against EGFR Mutant Lung Cancer
- PMID: 39044361
- PMCID: PMC11425210
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202310126
Targeting Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin-2 (TRPM2) Enhances Therapeutic Efficacy of Third Generation EGFR Inhibitors against EGFR Mutant Lung Cancer
Abstract
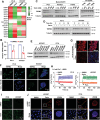
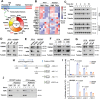
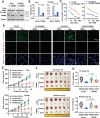
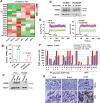
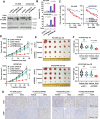
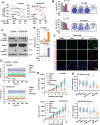
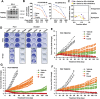
There is an urgent need to fully understand the biology of third generation EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs), particularly osimertinib, and to develop mechanism-driven strategies to manage their acquired resistance. Transient receptor potential melastatin-2 (TRPM2) functions as an important regulator of Ca2+ influx, but its role in mediating therapeutic efficacies of EGFR-TKIs and acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs has been rarely studied. This study has demonstrated a previously undiscovered role of suppression of TRPM2 and subsequent inhibition of Ca2+ influx and induction of ROS and DNA damage in mediating apoptosis induction and the therapeutic efficacy of osimertinib against EGFR mutant NSCLC. The rebound elevation represents a key mechanism accounting for the emergence of acquired resistance to osimertinib and other third generation EGFR-TKIs. Accordingly, targeting TRPM2 is a potentially promising strategy for overcoming and preventing acquired resistance to osimertinib, warranting further study in this direction including the development of cancer therapy-optimized TRPM2 inhibitors.
Keywords: EGFR‐TKIs; TRPM2; apoptosis; calcium; lung cancer; osimertinib.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
SSR is on consulting/advisory board for AstraZeneca, BMS, Merck, Roche, Tesaro and Amgen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ERK inhibition effectively overcomes acquired resistance of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells to osimertinib.Cancer. 2020 Mar 15;126(6):1339-1350. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32655. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31821539 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of hTERT/telomerase/telomere mediates therapeutic efficacy of osimertinib in EGFR mutant lung cancer.J Exp Med. 2024 Nov 4;221(11):e20240435. doi: 10.1084/jem.20240435. Epub 2024 Sep 19. J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39297884
-
Advancements in fourth-generation EGFR TKIs in EGFR-mutant NSCLC: Bridging biological insights and therapeutic development.Cancer Treat Rev. 2024 Nov;130:102824. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2024.102824. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Cancer Treat Rev. 2024. PMID: 39366135 Review.
-
Inhibition of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL overcomes the resistance to the third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jan;23(1):48. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11686. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33200796 Free PMC article.
-
Osimertinib and other third-generation EGFR TKI in EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients.Ann Oncol. 2018 Jan 1;29(suppl_1):i20-i27. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx704. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29462255 Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering the predictive and immunomodulatory potential of transient receptor potential melastatin family-related CCNE1 in pan-cancer.Mol Cancer. 2024 Nov 18;23(1):258. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02169-7. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39551726 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
