Ulcerative and pyogranulomatous pododermatitis due to Pseudomonas luteola infection in a domestic ferret (Mustela putorius furo): a case report with literature review of this emerging zoonotic disease in ferrets
- PMID: 39042223
- PMCID: PMC11442507
- DOI: 10.1007/s11259-024-10464-3
Ulcerative and pyogranulomatous pododermatitis due to Pseudomonas luteola infection in a domestic ferret (Mustela putorius furo): a case report with literature review of this emerging zoonotic disease in ferrets
Abstract
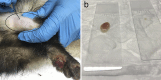
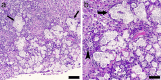
Pseudomonas luteola (P.luteola), formerly called Chryseomonas luteola, is a strict aerobic gram-negative bacillus, 0.8 to 1.0 µm wide and 1.5 to 2.5 µm long, considered an opportunistic pathogen found ubiquitously in humid environments, both in soil and water. It sporadically causes disease in animals and immunosuppressed humans or those subjected to invasive procedures such us peritoneal dialysis or catheterization. In ferrets, this infection was first described in Spain in 2012 and since then, cases have appeared occasionally in Finland, Austria, Australia, France, the United States and also in Spain. This pathogen is considered an emerging zoonotic disease in ferrets, causing respiratory disease, panniculitis, and abscesses due to pyogranulomatous or suppurative inflammation predominantly of the pleura, lung, mediastinum, panniculus or salivary glands, frequently with lethal consequences. The clinical case of a ferret, infected by Pseudomona luteola, presenting with ulcerative suppurative pododermatitis and ipsilateral popliteal purulent lymphadenitis, is described. Together with a complete resolution of the clinical case by means of a non-invasive medical management likely due to the rapid detection, identification, and treatment of the infection.
Keywords: Pseudomonas luteola; Ferret; Pododermatitis; Spain.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pyogranulomatous panniculitis in ferrets (Mustela putorius furo) with intralesional demonstration of Pseudomonas luteola.J Comp Pathol. 2015 Feb-Apr;152(2-3):114-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Feb 27. J Comp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25728813
-
Pyogranulomatous pleuropneumonia and mediastinitis in ferrets (Mustela putorius furo) associated with Pseudomonas luteola Infection.J Comp Pathol. 2012 Jan;146(1):4-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2011.03.014. Epub 2011 May 24. J Comp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 21601873 Free PMC article.
-
Pyogranulomatous panniculitis in a domestic cat associated with Pseudomonas luteola infection.Vet Dermatol. 2021 Feb;32(1):83-e15. doi: 10.1111/vde.12893. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Vet Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 32991013
-
Emerging Zoonotic Diseases in Ferrets.Vet Clin North Am Exot Anim Pract. 2020 May;23(2):299-308. doi: 10.1016/j.cvex.2020.01.012. Vet Clin North Am Exot Anim Pract. 2020. PMID: 32327037 Review.
-
Feral ferrets (Mustela furo) as hosts and sentinels of tuberculosis in New Zealand.N Z Vet J. 2015 Jun;63 Suppl 1(sup1):42-53. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2014.981314. Epub 2015 Mar 10. N Z Vet J. 2015. PMID: 25495945 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altinok I, Balta F, Capkin E, Kayis S (2007) Disease of rainbow trout caused by Pseudomonas luteola. Aquaculture 273:393–397
-
- Baum B, Richter B, Reifinger M, Klang A, Finnberg C, Loncaric I, Spergser J, Eisenberg T, Künzel F, Preis S, Pantchev N, Rütgen B, Guija de Arespacochaga A, Hewicker-Trautwein M (2015) Pyogranulomatous panniculitis in ferrets (Mustela putorius furo) with intralesional demonstration of Pseudomonas luteola. J Comp Pathol 152:114–118 - PubMed
-
- Bayhan GI, Senel S, Tanir G, Ozkan S (2015) Bacteremia caused by Pseudomonas luteola in pediatric patients. Jpn J Infect Dis 68:50–54 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

