Flow cytometry-based quantitative analysis of cellular protein expression in apoptosis subpopulations: A protocol
- PMID: 39040270
- PMCID: PMC11260931
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33665
Flow cytometry-based quantitative analysis of cellular protein expression in apoptosis subpopulations: A protocol
Abstract
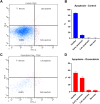
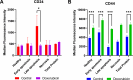
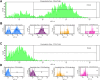
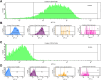
Flow cytometry techniques utilizing dual staining with annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) provide a robust method for quantitatively analyzing apoptosis induction. Annexin V binds phosphatidylserine exposed on the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane during early apoptosis, while PI permeates late apoptotic/necrotic cells. Simultaneous staining allows differentiation of viable, early apoptotic, and late apoptotic/necrotic populations. This approach can be enhanced by using fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies to stain specific proteins, enabling the simultaneous tracking of protein expression changes in defined cell subpopulations during apoptosis. This multiparametric approach provides key insights into signaling regulation and the mechanisms underlying the apoptotic response to cytotoxic treatments. Here we present a protocol that combines annexin V-FITC/PI staining with APC-conjugated antibody labeling in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells treated with doxorubicin. This protocol enables both the quantitative assessment of apoptosis induction and the tracking of decreased CD44 expression from viable to apoptotic cells. This protocol also provides guidelines for appropriate filter selection, compensation controls, gating strategies, and troubleshooting. This robust protocol holds significant potential for elucidating signaling networks involved in apoptosis and therapeutic resistance across various cellular models.
Keywords: Annexin V; Apoptosis; Flow cytometry; Propidium iodide; Protein expression.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitation of Apoptosis and Necrosis by Annexin V Binding, Propidium Iodide Uptake, and Flow Cytometry.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2016 Nov 1;2016(11). doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot087288. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2016. PMID: 27803250
-
Detection of apoptosis in ovarian cells in vitro and in vivo using the annexin v-affinity assay.Methods Mol Med. 2001;39:669-77. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-071-3:669. Methods Mol Med. 2001. PMID: 21340828
-
Modified annexin V/propidium iodide apoptosis assay for accurate assessment of cell death.J Vis Exp. 2011 Apr 24;(50):2597. doi: 10.3791/2597. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21540825 Free PMC article.
-
A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V.J Immunol Methods. 1995 Jul 17;184(1):39-51. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(95)00072-i. J Immunol Methods. 1995. PMID: 7622868
-
Expression and purification of recombinant annexin V for the detection of membrane alterations on apoptotic cells.Methods. 2008 Mar;44(3):235-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.11.010. Methods. 2008. PMID: 18314054 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

