Recent advances in the metamaterial and metasurface-based biosensor in the gigahertz, terahertz, and optical frequency domains
- PMID: 39040247
- PMCID: PMC11260956
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33272
Recent advances in the metamaterial and metasurface-based biosensor in the gigahertz, terahertz, and optical frequency domains
Abstract
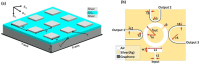
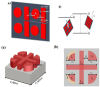
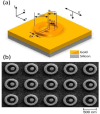
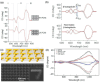
Recently, metamaterials and metasurface have gained rapidly increasing attention from researchers due to their extraordinary optical and electrical properties. Metamaterials are described as artificially defined periodic structures exhibiting negative permittivity and permeability simultaneously. Whereas metasurfaces are the 2D analogue of metamaterials in the sense that they have a small but not insignificant depth. Because of their high optical confinement and adjustable optical resonances, these artificially engineered materials appear as a viable photonic platform for biosensing applications. This review paper discusses the recent development of metamaterial and metasurface in biosensing applications based on the gigahertz, terahertz, and optical frequency domains encompassing the whole electromagnetic spectrum. Overlapping features such as material selection, structure, and physical mechanisms were considered during the classification of our biosensing applications. Metamaterials and metasurfaces working in the GHz range provide prospects for better sensing of biological samples, THz frequencies, falling between GHz and optical frequencies, provide unique characteristics for biosensing permitting the exact characterization of molecular vibrations, with an emphasis on molecular identification, label-free analysis, and imaging of biological materials. Optical frequencies on the other hand cover the visible and near-infrared regions, allowing fine regulation of light-matter interactions enabling metamaterials and metasurfaces to offer excellent sensitivity and specificity in biosensing. The outcome of the sensor's sensitivity to an electric or magnetic field and the resonance frequency are, in theory, determined by the frequency domain and features. Finally, the challenges and possible future perspectives in biosensing application areas have been presented that use metamaterials and metasurfaces across diverse frequency domains to improve sensitivity, specificity, and selectivity in biosensing applications.
Keywords: Biosensing; Frequency domain; Metamaterials; Metasurface; Sensor configuration.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Terahertz Metamaterials for Biosensing Applications: A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Dec 21;14(1):3. doi: 10.3390/bios14010003. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38275304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in terahertz metasurface graphene for biosensing and application.Discov Nano. 2023 Apr 15;18(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s11671-023-03814-8. eCollection 2023 Dec. Discov Nano. 2023. PMID: 37091985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasmonic Metamaterials for Nanochemistry and Sensing.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Nov 19;52(11):3018-3028. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00325. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31680511
-
Metasurface-Assisted Terahertz Sensing.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 25;23(13):5902. doi: 10.3390/s23135902. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37447747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Near-field Terahertz Sensing of HeLa Cells and Pseudomonas Based on Monolithic Integrated Metamaterials with a Spintronic Terahertz Emitter.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Aug 12;12(32):35895-35902. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c08543. Epub 2020 Aug 3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32643363
References
-
- Holloway C.L., Kuester E.F., Gordon J.I., O'Hara J.F., Booth J.T., Smith D.R. An overview of the theory and applications of metasurfaces the two-dimensional equivalents of metamaterials. IEEE Antenn. Propag. Mag. 2012;54(2):10–35. doi: 10.1109/map.2012.6230714. - DOI
-
- Yin S., Galiffi E., Alù A. Floquet metamaterials. eLight. 2022;2(1) doi: 10.1186/s43593-022-00015-1. - DOI
-
- Wen J., Ren Q., Ruiguang P., Yao H., Qing Y., Yin J., Zhao Q. Progress in water-based metamaterial absorbers a review. Opt. Mater. Express. 2022;12(4):1461. doi: 10.1364/ome.455723. - DOI
-
- Pendry J.B. Conference on Coherence and Quantum Optics. 2007. Metamaterials and the control of electromagnetic fields. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

