ATF3 is involved in rSjP40-mediated inhibition of HSCs activation in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice
- PMID: 39031798
- PMCID: PMC11190947
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.18458
ATF3 is involved in rSjP40-mediated inhibition of HSCs activation in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice
Abstract
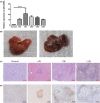
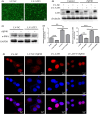
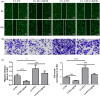
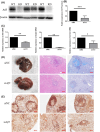
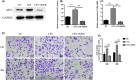
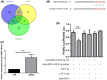
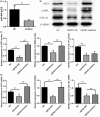
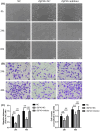
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease characterized by liver fibrosis, a process driven by the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and subsequent collagen production. Previous studies from our laboratory have demonstrated the ability of Schistosoma japonicum protein P40 (SjP40) to inhibit HSCs activation and exert an antifibrotic effect. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the molecular mechanism underlying the inhibitory effect of recombinant SjP40 (rSjP40) on HSCs activation. Using a cell model in which rSjP40 inhibited LX-2 cell activation, we performed RNA-seq analyses and identified ATF3 as the most significantly altered gene. Further investigation revealed that rSjP40 inhibited HSCs activation partly by suppressing ATF3 activation. Knockdown of ATF3 in mouse liver significantly alleviated S. japonicum-induced liver fibrosis. Moreover, our results indicate that ATF3 is a direct target of microRNA-494-3p, a microRNA associated with anti-liver fibrosis effects. rSjP40 was found to downregulate ATF3 expression by upregulating microRNA-494-3p in LX-2 cells. This downregulation led to the inhibition of the expression of liver fibrosis proteins α-SMA and COL1A1, ultimately alleviating liver fibrosis caused by S. japonicum.
Keywords: Schistosoma japonicum; ATF3; Schistosoma japonicum protein P40; hepatic stellate cell; microRNA‐494‐3p.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of let-7b in the inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation by rSjP40.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Jun 23;15(6):e0009472. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009472. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34161325 Free PMC article.
-
rSjP40 suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation by promoting microRNA-155 expression and inhibiting STAT5 and FOXO3a expression.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Nov;22(11):5486-5493. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13819. Epub 2018 Aug 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30091834 Free PMC article.
-
Schistosoma japonicum egg antigen up-regulates fibrogenesis and inhibits proliferation in primary hepatic stellate cells in a concentration-dependent manner.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb 28;19(8):1230-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1230. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23482848 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of cannabinoid receptor-1 and fibrotic activation of mouse hepatic stellate cells during Schistosoma J. infection: role of NADPH oxidase.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Jun;71:109-120. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.03.015. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24657416 Free PMC article.
-
Schistosoma japonicum protein SjP40 inhibits TGF-β1-induced activation of hepatic stellate cells.Parasitol Res. 2015 Nov;114(11):4251-7. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4663-0. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Parasitol Res. 2015. PMID: 26268567
References
-
- Zhang LJ, Xu ZM, Yang F, et al. Endemic status of schistosomiasis in People's Republic of China in 2020. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2021;33:225‐233. - PubMed
-
- Gryseels B, Polman K, Clerinx J, Kestens L. Human schistosomiasis. Lancet. 2006;368:1106‐1118. - PubMed
-
- Duan YN, Qian HY, Qin YW, et al. Dynamics of Sept4 expression in fibrotic livers of mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum. Parasitology. 2011;138:1003‐1010. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

