Alpha-lipoic acid alleviates cognitive deficits in transgenic APP23/PS45 mice through a mitophagy-mediated increase in ADAM10 α-secretase cleavage of APP
- PMID: 39030577
- PMCID: PMC11264788
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-024-01527-3
Alpha-lipoic acid alleviates cognitive deficits in transgenic APP23/PS45 mice through a mitophagy-mediated increase in ADAM10 α-secretase cleavage of APP
Abstract
Background: Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) has a neuroprotective effect on neurodegenerative diseases. In the clinic, ALA can improve cognitive impairments in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other dementias. Animal studies have confirmed the anti-amyloidosis effect of ALA, but its underlying mechanism remains unclear. In particular, the role of ALA in amyloid-β precursor protein (APP) metabolism has not been fully elucidated.
Objective: To investigate whether ALA can reduce the amyloidogenic effect of APP in a transgenic mouse model of AD, and to study the mechanism underlying this effect.
Methods: ALA was infused into 2-month-old APP23/PS45 transgenic mice for 4 consecutive months and their cognitive function and AD-like pathology were then evaluated. An ALA drug concentration gradient was applied to 20E2 cells in vitro to evaluate its effect on the expression of APP proteolytic enzymes and metabolites. The mechanism by which ALA affects APP processing was studied using GI254023X, an inhibitor of A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase 10 (ADAM10), as well as the mitochondrial toxic drug carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP).
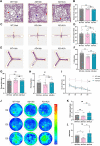
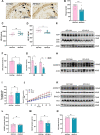
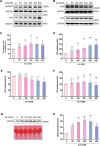
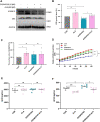
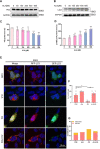
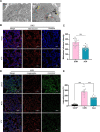
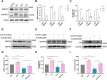
Results: Administration of ALA ameliorated amyloid plaque neuropathology in the brain tissue of APP23/PS45 mice and reduced learning and memory impairment. ALA also increased the expression of ADAM10 in 20E2 cells and the non-amyloidogenic processing of APP to produce the 83 amino acid C-terminal fragment (C83). In addition to activating autophagy, ALA also significantly promoted mitophagy. BNIP3L-knockdown reduced the mat/pro ratio of ADAM10. By using CCCP, ALA was found to regulate BNIP3L-mediated mitophagy, thereby promoting the α-cleavage of APP.
Conclusions: The enhanced α-secretase cleavage of APP by ADAM10 is the primary mechanism through which ALA ameliorates the cognitive deficits in APP23/PS45 transgenic mice. BNIP3L-mediated mitophagy contributes to the anti-amyloid properties of ALA by facilitating the maturation of ADAM10. This study provides novel experimental evidence for the treatment of AD with ALA.
Keywords: AD; ADAM10; ALA; Cognitive deficits; Mitophagy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gallic acid is a dual α/β-secretase modulator that reverses cognitive impairment and remediates pathology in Alzheimer mice.J Biol Chem. 2020 Nov 27;295(48):16251-16266. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.012330. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32913125 Free PMC article.
-
SIL1 improves cognitive impairment in APP23/PS45 mice by regulating amyloid precursor protein processing and Aβ generation.Zool Res. 2024 Jul 18;45(4):845-856. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2023.363. Zool Res. 2024. PMID: 39004862 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Lactoferrin Enhances α-Secretase-Dependent Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing via the ERK1/2-CREB and HIF-1α Pathways in an Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017 Dec;42(13):2504-2515. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.8. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28079060 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the anti-amyloidogenic secretase ADAM10 in shedding the APP-like proteins.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012 Feb;9(2):157-64. doi: 10.2174/156720512799361664. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012. PMID: 21605036 Review.
-
ADAM10 in Alzheimer's disease: Pharmacological modulation by natural compounds and its role as a peripheral marker.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 May;113:108661. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108661. Epub 2019 Mar 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30836275 Review.
References
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology. 1984;34(7):939–44. 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

