The inflammatory and metabolic status of patients with sudden-onset sensorineural hearing loss
- PMID: 39015324
- PMCID: PMC11250376
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1382096
The inflammatory and metabolic status of patients with sudden-onset sensorineural hearing loss
Abstract
Introduction: Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is a common emergency symptom in otolaryngology that requires immediate diagnosis and treatment. SSNHL has a multifactorial etiology, and its pathophysiologic mechanisms may be associated with inflammatory and metabolic changes that may affect the cochlear microenvironment or its nervous component, thus triggering the process or hindering hearing recovery. Therefore, the aim of this study was to assess metabolic and inflammatory changes to identify systemic parameters that could serve as prognostic factors for hearing recovery in patients with SSNHL.
Materials and methods: Thirty patients with a sudden hearing loss of at least 30 dB in three contiguous frequencies were enrolled in this study. Patients were followed up for 4 months and peripheral blood samples were collected at 7 days (V1), 30 days (V2) and 120 days (V3). Interleukins (IL)-1F7, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, interferon γ (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and adiponectin were quantified in serum. In addition, lipid and glycemic profiles as well as concentration of creatinine, uric acid, fructosamine, peroxide, total proteins and albumin were analyzed. Patients underwent weekly ear-specific hearing tests with standard pure tone thresholds for frequencies of 250-8,000 Hz, speech recognition threshold and word recognition score.
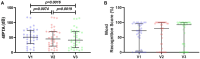
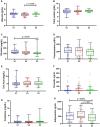
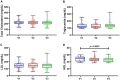
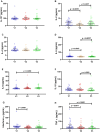
Results: Patients with SSNHL were divided into a group of patients who did not achieve hearing recovery (n = 14) and another group who achieved complete and significant recovery (n = 16). Most serologic parameters showed no significant changes or values indicating clinical changes. However, IFN-γ levels decreased by 36.3% between V1 and V2. The cytokine TNF-α showed a statistically significant decrease from V1 to V3 (from 22.91 to 10.34 pg./mL). Adiponectin showed a decrease from 553.7 ng/mL in V1 to 454.4 ng/mL in V3.
Discussion: Our results show that serologic cytokine levels change in the acute phase of manifestation of SSNHL and establish a parallel between systemic changes and improvements in hearing, especially TNF-α, which showed differences in hearing recovery. The use of IFN-γ, TNF-α and adiponectin may elucidate the clinical improvement in these patients.
Keywords: IFNγ; TNF-α; adiponectin; cytokines; inflammation; metabolism; sudden sensorineural hearing loss.
Copyright © 2024 do Amaral, Peron, Soeiro, Scott, Hortense, da Silva, França, Nali, Bachi and de Oliveira Penido.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical features and prognosis of severe-to-profound sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Am J Otolaryngol. 2022 May-Jun;43(3):103455. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103455. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Am J Otolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35398740
-
Clinical Value of a Novel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protocol and Prognostic Model Establishment for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Prospective Study.Audiol Neurootol. 2023;28(2):138-150. doi: 10.1159/000527738. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Audiol Neurootol. 2023. PMID: 36513028 Free PMC article.
-
Digging into the Role of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jul 20;58(7):963. doi: 10.3390/medicina58070963. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35888682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Factors in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Balkan Med J. 2016 Jan;33(1):87-93. doi: 10.5152/balkanmedj.2015.15216. Epub 2016 Jan 1. Balkan Med J. 2016. PMID: 26966623 Free PMC article.
-
Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy.Laryngoscope. 2007 Jan;117(1):3-15. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000245058.11866.15. Laryngoscope. 2007. PMID: 17202923 Review.
References
-
- Castellucci A, Botti C, Delmonte S, Bettini M, Lusetti F, Brizzi P, et al. . Vestibular assessment in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: role in the prediction of hearing outcome and in the early detection of vascular and hydropic pathomechanisms. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1127008. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1127008, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

