This is a preprint.
PRDM16-DT: A Brain and Astrocyte-Specific lncRNA Implicated in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 39005272
- PMCID: PMC11244882
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.27.600964
PRDM16-DT: A Brain and Astrocyte-Specific lncRNA Implicated in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
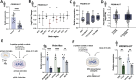
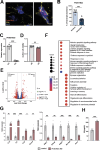
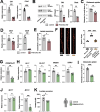
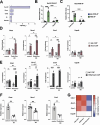
Astrocytes provide crucial support for neurons, contributing to synaptogenesis, synaptic maintenance, and neurotransmitter recycling. Under pathological conditions, deregulation of astrocytes contributes to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), highlighting the growing interest in targeting astrocyte function to address early phases of AD pathogenesis. While most research in this field has focused on protein-coding genes, non-coding RNAs, particularly long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), have emerged as significant regulatory molecules. In this study, we identified the lncRNA PRDM16-DT as highly enriched in the human brain, where it is almost exclusively expressed in astrocytes. PRDM16-DT and its murine homolog, Prdm16os, are downregulated in the brains of AD patients and in AD models. In line with this, knockdown of PRDM16-DT and Prdm16os revealed its critical role in maintaining astrocyte homeostasis and supporting neuronal function by regulating genes essential for glutamate uptake, lactate release, and neuronal spine density through interactions with the RE1-Silencing Transcription factor (Rest) and Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2). Notably, CRISPR-mediated overexpression of Prdm16os mitigated functional deficits in astrocytes induced by stimuli linked to AD pathogenesis. These findings underscore the importance of PRDM16-DT in astrocyte function and its potential as a novel therapeutic target for neurodegenerative disorders characterized by astrocyte dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures

Similar articles
-
PRDM16-DT is a novel lncRNA that regulates astrocyte function in Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Aug 29;148(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02787-x. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 39207536 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional diversification and neurodegenerative diseases.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Aug;97:69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23756188 Review.
-
Semaphorin 4D is upregulated in neurons of diseased brains and triggers astrocyte reactivity.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Aug 6;19(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02509-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35933420 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte energy and neurotransmitter metabolism in Alzheimer's disease: Integration of the glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle.Prog Neurobiol. 2022 Oct;217:102331. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2022.102331. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Prog Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35872221 Review.
-
The lncRNA Neat1 is associated with astrocyte reactivity and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 3:2023.05.03.539260. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.03.539260. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37205548 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
