SIL1 improves cognitive impairment in APP23/PS45 mice by regulating amyloid precursor protein processing and Aβ generation
- PMID: 39004862
- PMCID: PMC11298678
- DOI: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2023.363
SIL1 improves cognitive impairment in APP23/PS45 mice by regulating amyloid precursor protein processing and Aβ generation
Abstract
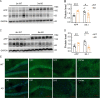
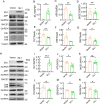
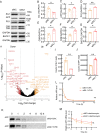
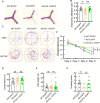
SIL1, an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident protein, is reported to play a protective role in Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the effect of SIL1 on amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing remains unclear. In this study, the role of SIL1 in APP processing was explored both in vitro and in vivo. In the in vitro experiment, SIL1 was either overexpressed or knocked down in cells stably expressing the human Swedish mutant APP695. In the in vivo experiment, AAV-SIL1-EGFP or AAV-EGFP was microinjected into APP23/PS45 mice and their wild-type littermates. Western blotting (WB), immunohistochemistry, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), and behavioral experiments were performed to evaluate the relevant parameters. Results indicated that SIL1 expression decreased in APP23/PS45 mice. Overexpression of SIL1 significantly decreased the protein levels of APP, presenilin-1 (PS1), and C-terminal fragments (CTFs) of APP in vivo and in vitro. Conversely, knockdown of SIL1 increased the protein levels of APP, β-site APP cleavage enzyme 1 (BACE1), PS1, and CTFs, as well as APP mRNA expression in 2EB2 cells. Furthermore, SIL1 overexpression reduced the number of senile plaques in APP23/PS45 mice. Importantly, Y-maze and Morris Water maze tests demonstrated that SIL1 overexpression improved cognitive impairment in APP23/PS45 mice. These findings indicate that SIL1 improves cognitive impairment in APP23/PS45 mice by inhibiting APP amyloidogenic processing and suggest that SIL1 is a potential therapeutic target for AD by modulating APP processing.
SIL1是一种内质网驻留蛋白, 已被报道在阿尔茨海默症中发挥保护作用。然而,SIL1对APP代谢的影响还不清楚。在该研究中,我们从体内外都探索了SIL1对APP代谢的影响。 在体外实验中,我们在稳转了Swedish突变的APP695细胞系中过表达或敲低SIL1。在体内实验中,我们在APP23/PS45小鼠及其同窝的野生型小鼠侧脑室中注射对照或带有SIL1过表达的腺相关病毒。我们采用蛋白免疫印迹,免疫组化,RNA测序,以及行为学等实验方法来进行相关检测。我们发现,SIL1蛋白水平在APP23/PS45小鼠中明显减少。而在体内外过表达SIL1后明显减少APP、PS1和CTFs的蛋白水平。相反,敲低SIL1后明显增加了APP、BACE1、PS1和CTFs的蛋白水平,以及APP的mRNA水平。此外,SIL1过表达减少了APP23/PS45小鼠的老年斑。更重要的是,Y-迷宫和水迷宫的结果显示SIL1过表达明显改善了APP23/PS45小鼠的认知损害。我们的结果表明,SIL1通过抑制APP的淀粉样代谢改善了APP23/PS45小鼠的认知损害,并且提示了SIL1可作为调节APP代谢治疗阿尔茨海默症的潜在靶点。.
Keywords: APP processing; Alzheimer’s disease; Cognitive impairment; SIL1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alpha-lipoic acid alleviates cognitive deficits in transgenic APP23/PS45 mice through a mitophagy-mediated increase in ADAM10 α-secretase cleavage of APP.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Jul 19;16(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01527-3. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39030577 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Sailuotong on neurovascular unit in amyloid precursor protein/presenilin-1 transgenic mice with Alzheimer's disease.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Apr;44(2):289-302. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240203.007. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38504535 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin 1 regulates the processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragments and the generation of amyloid beta-protein in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi.Biochemistry. 1998 Nov 24;37(47):16465-71. doi: 10.1021/bi9816195. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9843412
-
27-hydroxycholesterol promotes Aβ accumulation via altering Aβ metabolism in mild cognitive impairment patients and APP/PS1 mice.Brain Pathol. 2019 Jul;29(4):558-573. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12698. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Brain Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30582229 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism of presenilin 1: influence of presenilin 1 on amyloid precursor protein processing.Neurobiol Aging. 1998 Jan-Feb;19(1 Suppl):S15-8. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(98)00026-8. Neurobiol Aging. 1998. PMID: 9562461 Review.
References
-
-
Bourdenx M, Martín-Segura A, Scrivo A, et al. 2021. Chaperone-mediated autophagy prevents collapse of the neuronal metastable proteome.
Cell ,184 (10): 2696–2714. e25.
-
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
