Association between neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR) and depression symptoms among the United States adults: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 39003458
- PMCID: PMC11245866
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-024-02204-y
Association between neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR) and depression symptoms among the United States adults: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Depression acts as a noteworthy worldwide public health challenge. Identifying accessible biomarkers is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention. The relationship between depression in adult Americans and the neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR) was investigated in this research.
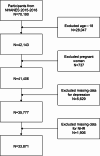
Methods: The relationship between NHR and depressive symptoms was analyzed utilizing National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data from 2005 to 2018 and the Patient Health Questionnaire-9. The study included 33,871 participants with complete NHR and depression data. Adjusted multivariable logistic regression models were used to account for possible confounders, and subgroup analyses were conducted to investigate effect changes.
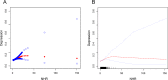
Results: Elevated NHR levels were positively correlated with a heightened risk of depression (OR = 1.03, 95% CI: 1.01-1.05, P < 0.0005). After the NHR was divided into tertiles, those in the top tertile had an 18% higher chance of developing depression than those in the bottom tertile (OR = 1.18; 95% CI: 1.05-1.32; P for trend = 0.0041). Subgroup analyses revealed variations in this association based on race and marital status. Additionally, the relationship between NHR and depression demonstrated a U-shaped pattern, with a significant breakpoint identified at an NHR of 6.97.
Conclusion: These results imply that the NHR may be a potential biomarker for depression risk, with implications for early detection and personalized treatment. Further research is needed to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the NHR-depression link and establish causality.
Keywords: Cross-sectional analysis; Depression; NHANES; Neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between Neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio and gallstones: insights from the national health and nutrition examination survey (2017-2020).Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Oct 31;23(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02349-w. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39482705 Free PMC article.
-
Association between high-density lipoprotein-related inflammation index and periodontitis: insights from NHANES 2009-2014.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Sep 28;23(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02312-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39342327 Free PMC article.
-
Association between neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and liver fibrosis in the US population: a nationally representative cross-sectional study using NHANES data from 2017 to 2020.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 5;24(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03394-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39237899 Free PMC article.
-
Association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) and the risk of post-stroke depression: A cross-sectional study.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024 Nov;33(11):107991. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2024.107991. Epub 2024 Sep 1. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 39227001
-
Utility of neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio in patients with coronary artery disease: a narrative review.J Int Med Res. 2023 Apr;51(4):3000605231166518. doi: 10.1177/03000605231166518. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37038922 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) and angina pectoris in US adults: a cross-sectional retrospective study based on NHANES 2009-2018.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Oct 26;23(1):347. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02343-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39462375 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio and gallstones: insights from the national health and nutrition examination survey (2017-2020).Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Oct 31;23(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02349-w. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39482705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang AA, Huang SY. Increased vigorous exercise and decreased sedentary activities are associated with decreased depressive symptoms in United States adults: analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2017–2020. Health Sci Rep. 2023;6(8):e1473. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1473. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical