Sorcin Inhibits Mitochondrial Apoptosis by Interacting with STAT3 via NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 39000312
- PMCID: PMC11241191
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25137206
Sorcin Inhibits Mitochondrial Apoptosis by Interacting with STAT3 via NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
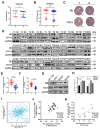
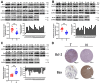
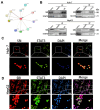
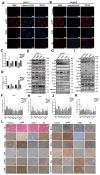
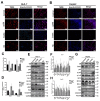
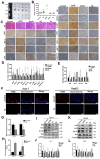
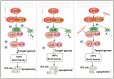
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common tumor. Our group has previously reported that sorcin (SRI) plays an important role in the progression and prognosis of HCC. This study aims to explore the mechanism of SRI inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptosis. Bioinformatics analysis, co-IP and immunofluorescence were used to analyze the relationship between SRI and STAT3. MMP and Hoechst staining were performed to detect the effect of SRI on cell apoptosis. The expression of apoptosis-related proteins and NF-κB signaling pathway were examined by Western blot and immunohistochemistry when SRI overexpression or underexpression in vivo and in vitro were found. Moreover, inhibitors were used to further explore the molecular mechanism. Overexpression of SRI inhibited cell apoptosis, which was attenuated by SRI knockdown in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, we identified that STAT3 is an SRI-interacting protein. Mechanistically, SRI interacts with STAT3 and then activates the NF-κB signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. SRI interacting with STAT3 inhibits apoptosis by the NF-κB pathway and further contributes to the proliferation in HCC, which offers a novel clue and a new potential therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: SRI; STAT3; apoptosis; protein–protein interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NCAPG2 overexpression promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis through activating the STAT3 and NF-κB/miR-188-3p pathways.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jun;44:237-249. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.05.053. Epub 2019 Jun 5. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31176678 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 1 as a novel tumor suppressor through selective downregulation of CSNK2B blocks nuclear factor-κB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma.EBioMedicine. 2020 Jan;51:102603. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.102603. Epub 2020 Jan 3. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 31901862 Free PMC article.
-
A Positive Feedback Loop of AKR1C3-Mediated Activation of NF-κB and STAT3 Facilitates Proliferation and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 1;81(5):1361-1374. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2480. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33361392
-
Anticancer activity of dietary xanthone α-mangostin against hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibition of STAT3 signaling via stabilization of SHP1.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jan 24;11(1):63. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2227-4. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 31980595 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 signaling pathway in inflammation, survival, proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1835(1):46-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.10.002. Epub 2012 Oct 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23103770 Review.
References
-
- Jühling F., Hamdane N., Crouchet E., Li S., El Saghire H., Mukherji A., Fujiwara N., A Oudot M., Thumann C., Saviano A., et al. Targeting clinical epigenetic reprogramming for chemoprevention of metabolic and viral hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2021;70:157–169. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318918. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Galarreta M.R., Bresnahan E., Molina-Sánchez P., Lindblad K.E., Maier B., Sia D., Puigvehi M., Miguela V., Casanova-Acebes M., Dhainaut M., et al. β-Catenin Activation Promotes Immune Escape and Resistance to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:1124–1141. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0074. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

