SnoRNAs: Exploring Their Implication in Human Diseases
- PMID: 39000310
- PMCID: PMC11240930
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25137202
SnoRNAs: Exploring Their Implication in Human Diseases
Abstract
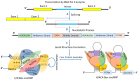
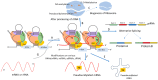
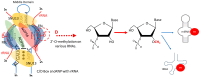
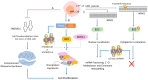
Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are earning increasing attention from research communities due to their critical role in the post-transcriptional modification of various RNAs. These snoRNAs, along with their associated proteins, are crucial in regulating the expression of a vast array of genes in different human diseases. Primarily, snoRNAs facilitate modifications such as 2'-O-methylation, N-4-acetylation, and pseudouridylation, which impact not only ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and their synthesis but also different RNAs. Functionally, snoRNAs bind with core proteins to form small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins (snoRNPs). These snoRNAs then direct the protein complex to specific sites on target RNA molecules where modifications are necessary for either standard cellular operations or the regulation of pathological mechanisms. At these targeted sites, the proteins coupled with snoRNPs perform the modification processes that are vital for controlling cellular functions. The unique characteristics of snoRNAs and their involvement in various non-metabolic and metabolic diseases highlight their potential as therapeutic targets. Moreover, the precise targeting capability of snoRNAs might be harnessed as a molecular tool to therapeutically address various disease conditions. This review delves into the role of snoRNAs in health and disease and explores the broad potential of these snoRNAs as therapeutic agents in human pathologies.
Keywords: RNA processing; human pathologies; small non-coding nucleolar RNA; small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins; snoRNA biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Small nucleolar RNAs: versatile trans-acting molecules of ancient evolutionary origin.Gene Expr. 2002;10(1-2):17-39. Gene Expr. 2002. PMID: 11868985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AtNUFIP, an essential protein for plant development, reveals the impact of snoRNA gene organisation on the assembly of snoRNPs and rRNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J. 2011 Mar;65(5):807-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04468.x. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Plant J. 2011. PMID: 21261762
-
SnoRNA microarray analysis reveals changes in H/ACA and C/D RNA levels caused by dyskerin ablation in mouse liver.Biochem J. 2010 Jul 1;429(1):33-41. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091898. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 20423331 Free PMC article.
-
[Small nucleolar RNAs].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2007 Mar-Apr;41(2):246-59. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2007. PMID: 17514894 Review. Russian.
-
Regulatory role of small nucleolar RNAs in human diseases.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:206849. doi: 10.1155/2015/206849. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26060813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bellodi C., McMahon M., Contreras A., Juliano D., Kopmar N., Nakamura T., Maltby D., Burlingame A., Savage S.A., Shimamura A., et al. H/ACA small RNA dysfunctions in disease reveal key roles for noncoding RNA modifications in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation. Cell Rep. 2013;3:1493–1502. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.04.030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

